Last November, we created the MacStories Setups page. It’s a collection of the gear, apps, and services that Federico and I use for work and play. We knew when we created the page that it would change regularly, and it has. Today, we’re introducing our third update in four months, which collects changes related to Federico’s MacPad setup and some smaller adjustments that we’ve both made recently.
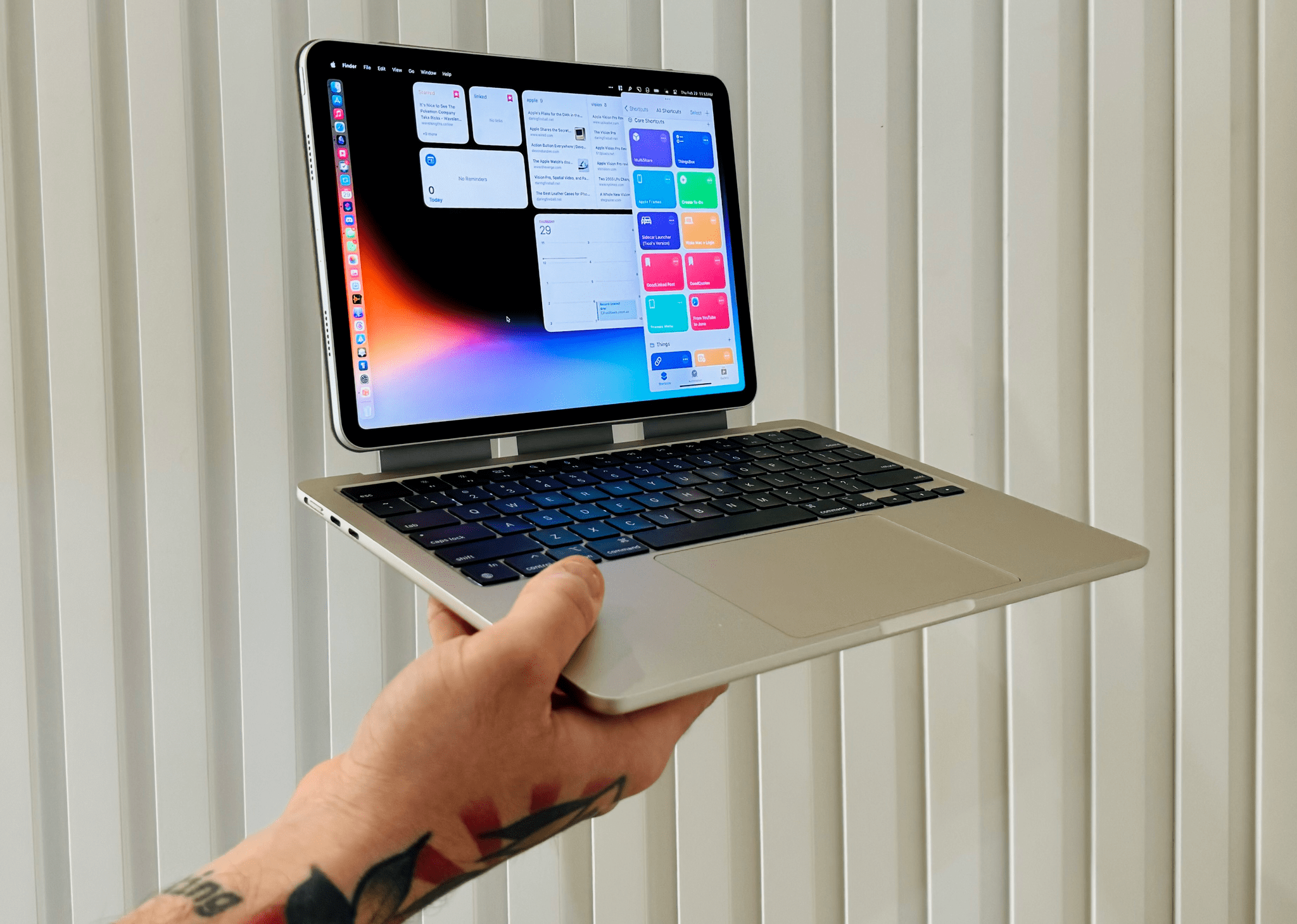
The MacPad additions to Federico’s setup include:
However, Federico isn’t living a MacPad-only lifestyle. He uses the Vision Pro daily and has added it along with the following accessories to his setup:
Other additions include:
Our app lineups change constantly, too, and most recently, Federico has added:
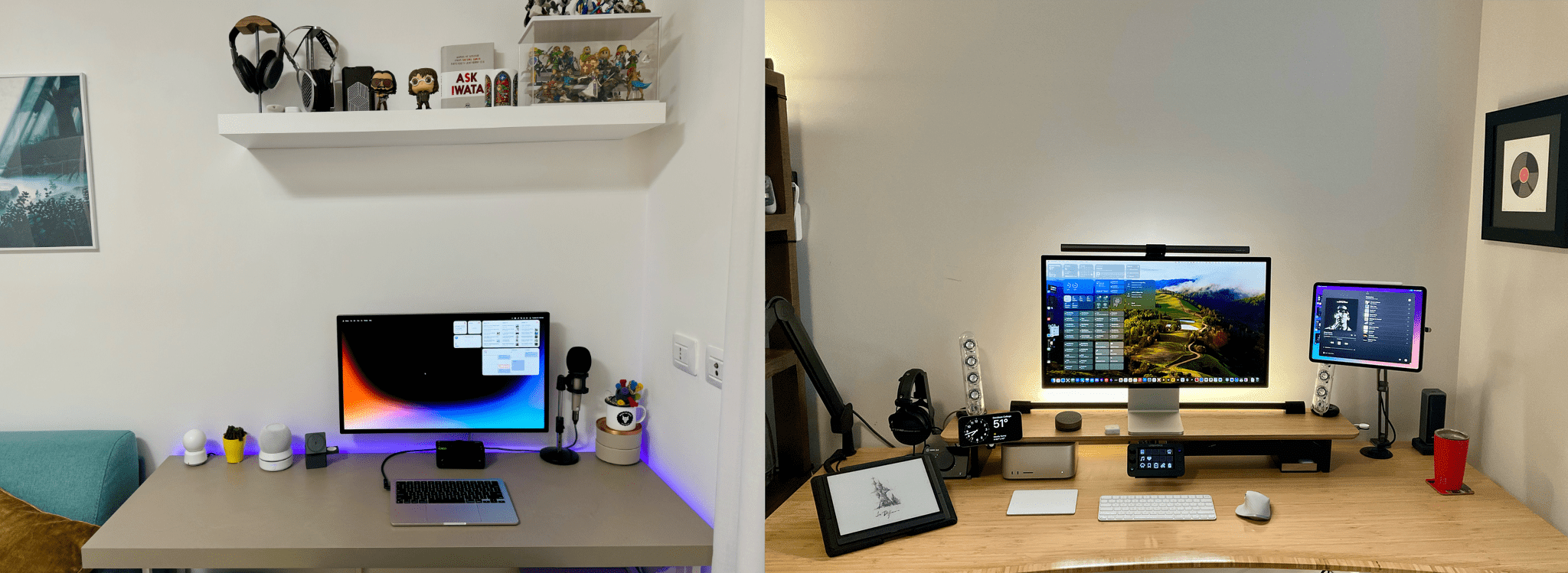
As for me, since my big desk setup upgrade, I’ve made a handful of changes to my desk and gaming setups, along with other adjustments.
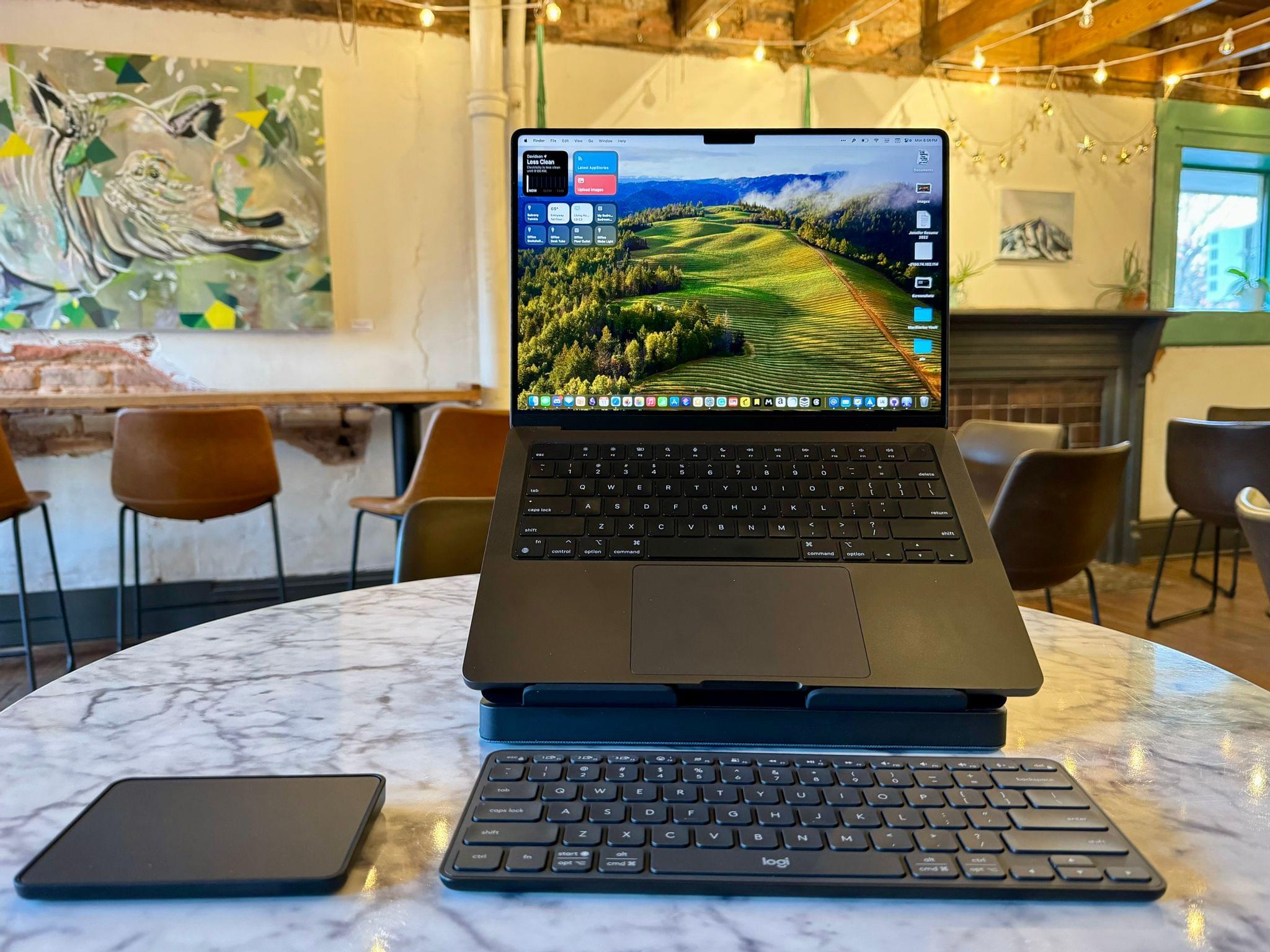
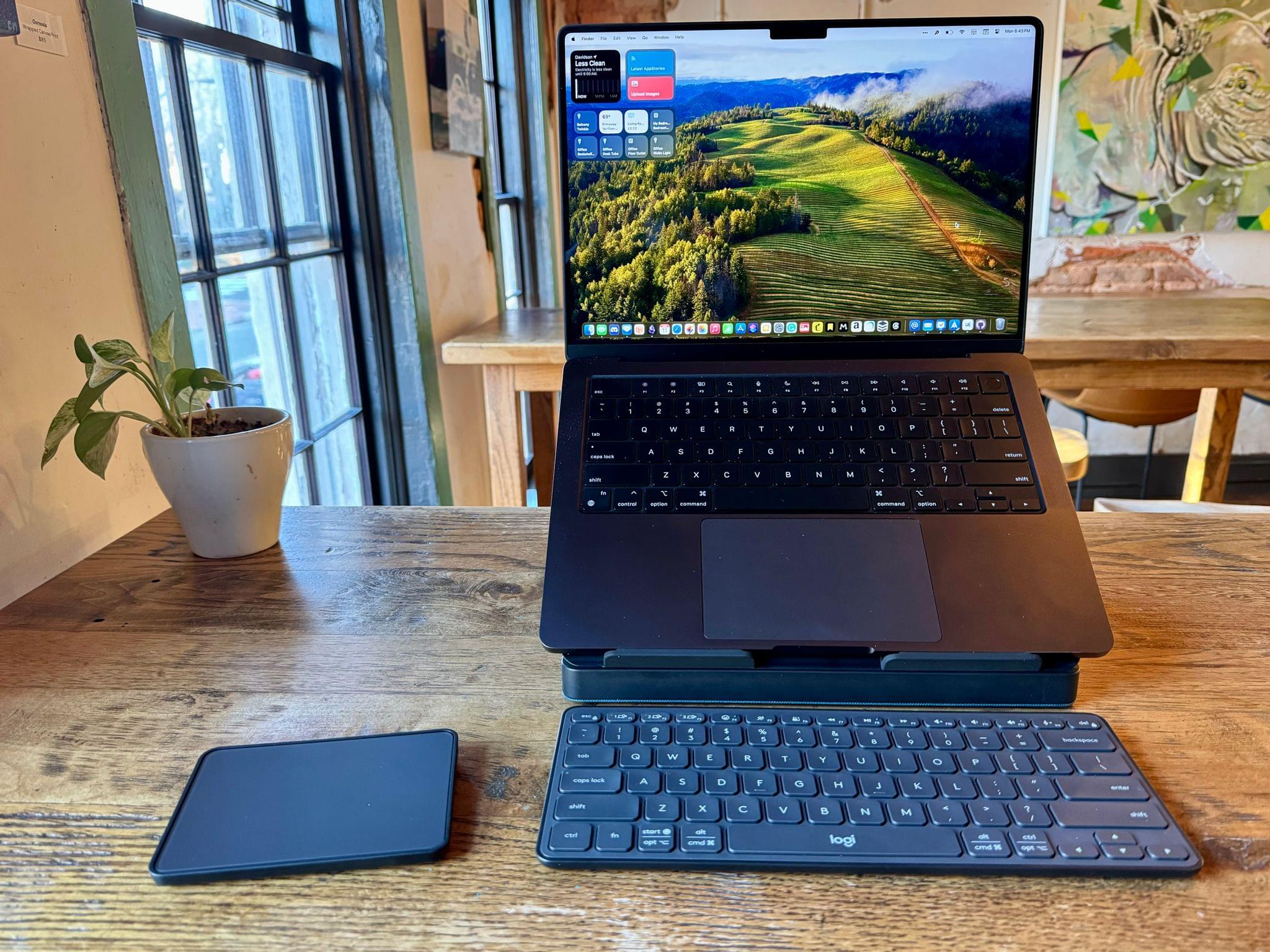
With summer around the corner, I’ve been refining my portable setup. The Logitech Casa Pop Up Desk that I reviewed recently is perfect for an afternoon at a coffee shop or sitting out on my balcony. I’ve enjoyed the Boox Tab Ultra so much that I added a Boox Palma for ultra-portable e-ink reading on-the-go.
The articles I save to read on the Palma and elsewhere are currently split between GoodLinks and Readwise Reader. I’ve also swapped out NaturalReader for Speechify for text-to-speech workflows, but I’m not completely satisfied with any read-aloud solution I’ve tried yet.
I’m also slowly refining my gaming setup. The ASUS ZenWiFi Pro Wi-Fi 6E mesh router system is a big step up from the Linksys Atlas routers I was using before in terms of both coverage and speed. I’m still floored by the bandwidth I get with my iPhone 15 Pro Max and Ayn Odin 2 Pro. I also picked up a Miyoo Mini+ retro gaming handheld because I’m traveling soon and wanted an ultra-portable handheld to take with me. Also, to track what I’m playing, I’ve been using GameTrack, which I recently reviewed.
Both of us have added a handful of other apps and gear, too, so be sure to browse through the Setups page to find the complete listing of our current setups.






](https://cdn.macstories.net/banneras-1629219199428.png)


.](https://cdn.macstories.net/169639-connectix-virtual-game-station-1711386686117.png)