Thursday is Global Accessibility Awareness Day. To mark the occasion, Apple has announced a long list of accessibility features coming to its products later this year and shared other ways it is celebrating the day through its apps and services.
Apple’s press release sums up the features coming to the iPhone, iPad, Mac, and Apple Watch as follows:
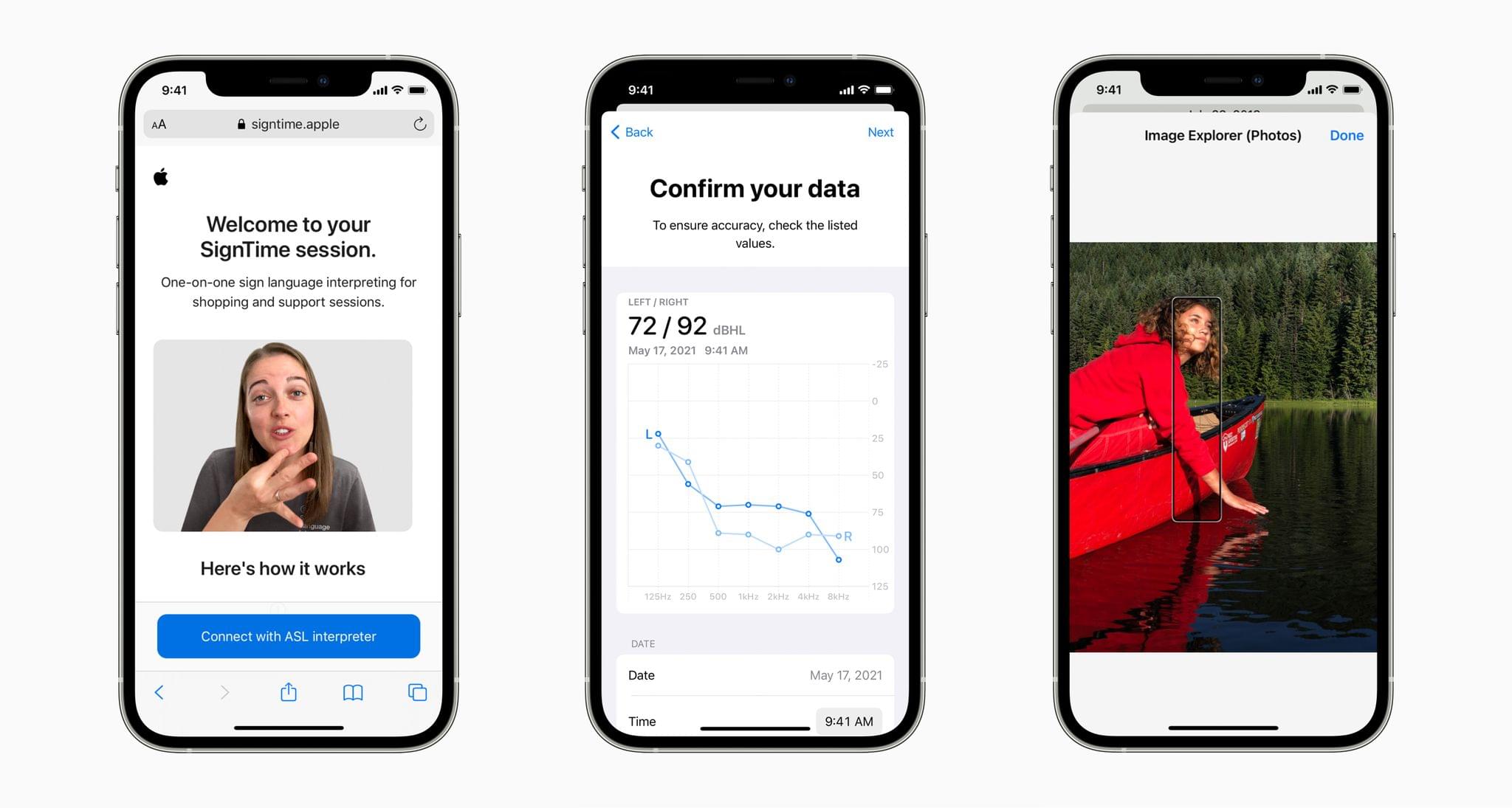
Using advancements across hardware, software, and machine learning, people who are blind or low vision can use their iPhone and iPad to navigate the last few feet to their destination with Door Detection; users with physical and motor disabilities who may rely on assistive features like Voice Control and Switch Control can fully control Apple Watch from their iPhone with Apple Watch Mirroring; and the Deaf and hard of hearing community can follow Live Captions on iPhone, iPad, and Mac. Apple is also expanding support for its industry-leading screen reader VoiceOver with over 20 new languages and locales. These features will be available later this year with software updates across Apple platforms.
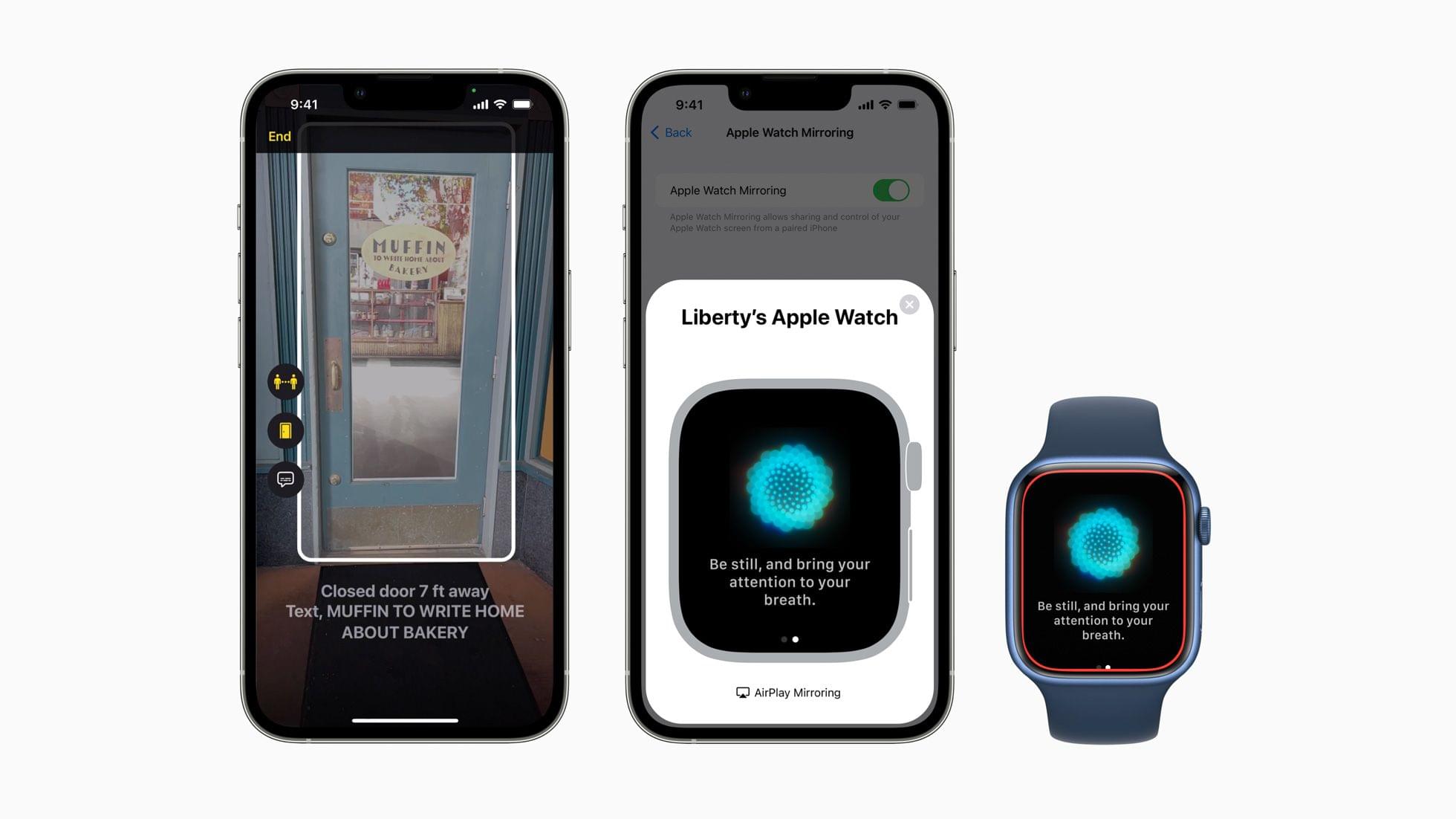
Door Detection will be part of the Magnifier app later this year. The feature helps blind and low vision users find and navigate doors when they arrive somewhere. The feature will judge the distance to the door using LiDAR, describe the door’s attributes, like whether it opens by pushing or using a doorknob, and read signs and symbols next to doors.
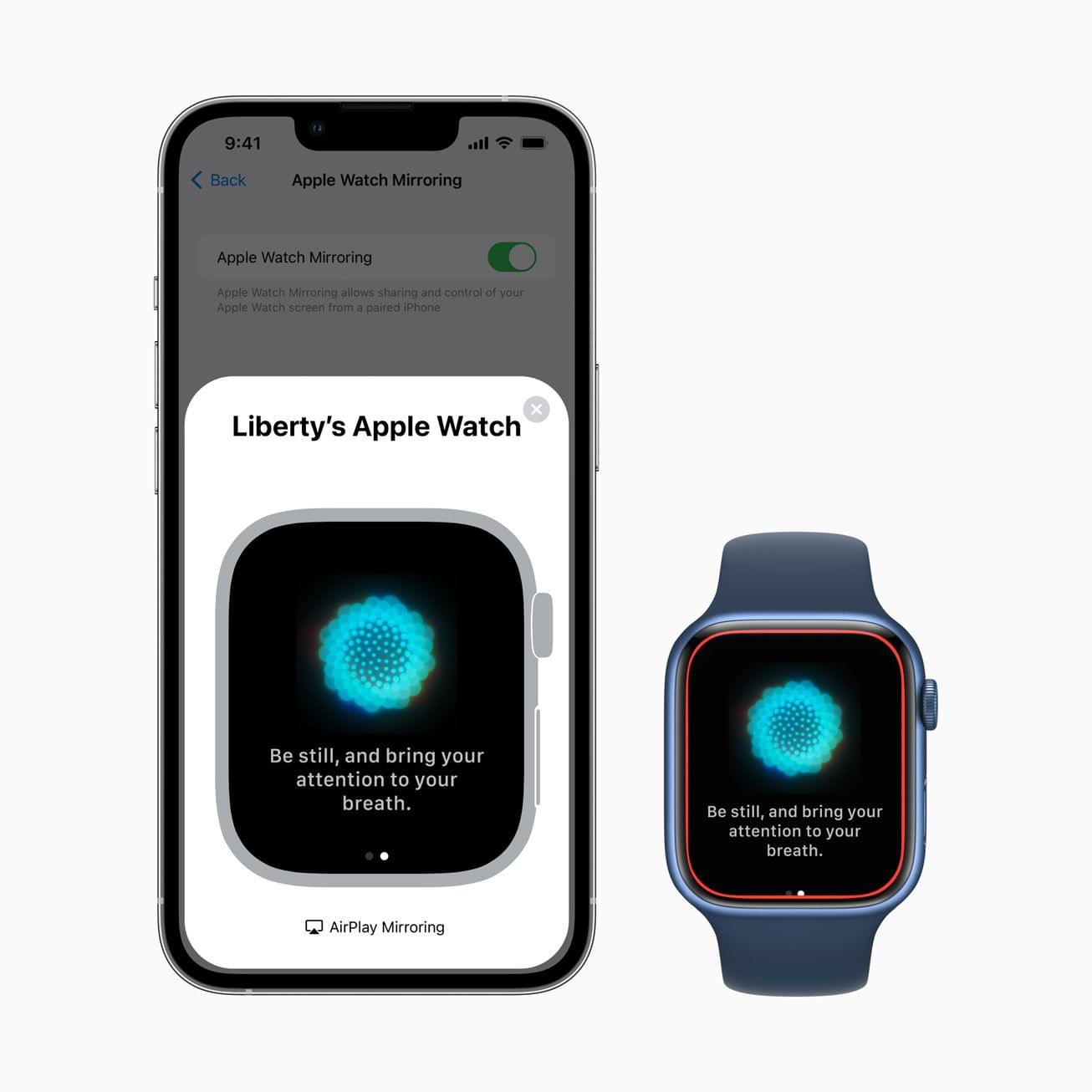
The Apple Watch will add several Physical and Motor accessibility features too. Apple Watch Mirroring, which is built on AirPlay in part, will allow users with physical and motor disabilities to control their Watches from an iPhone using Voice Control, Switch Control, voice commands, sound actions, head tracking, and Made for iPhone switches. The Apple Watch will also add a new double pinch gesture for controlling, like answering and ending phone calls and taking photos.
For Deaf and hard of hearing users, Apple will add Live Captions on the iPhone, iPad, and Mac. Apple says captioning will work with video calling apps like FaceTime, streaming video services, video conferencing apps, and in-person conversations. Live Captions occur on-device to preserve privacy, and on the Mac, users will be able to type a response that will be spoken aloud.
VoiceOver will get an update, too, adding the following languages:
- Arabic (World)
- Basque
- Bengali (India)
- Bhojpuri (India)
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Croatian
- Farsi
- French (Belgium)
- Galician
- Kannada
- Malay
- Mandarin (Liaoning, Shaanxi, Sichuan)
- Marathi
- Shanghainese (China)
- Spanish (Chile)
- Slovenian
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Ukrainian
- Valencian
- Vietnamese
VoiceOver on the Mac will also gain Text Checker that will discover formatting issues.
Apple previewed several other upcoming accessibility features across its products, including:
- Buddy Controller, the ability for someone to use a second game controller to assist with playing a game as though the two controllers were one
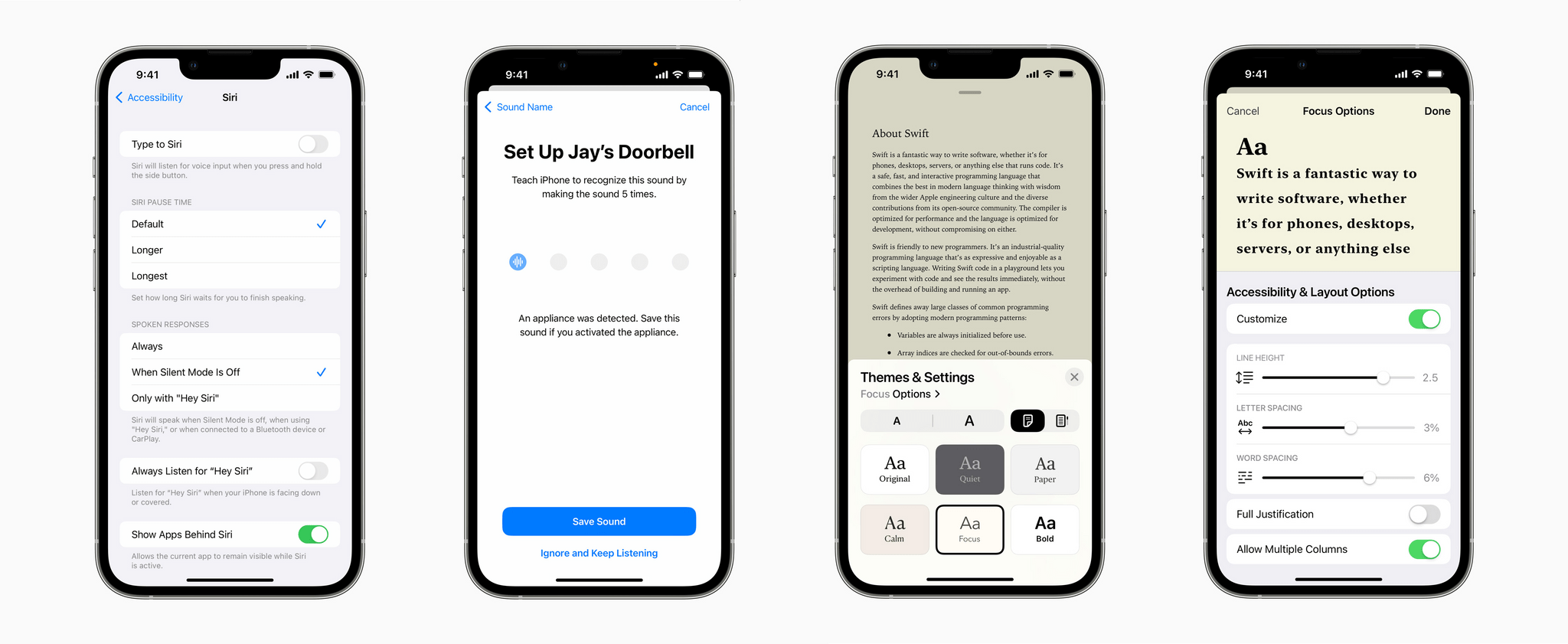
- Siri Pause Time, which will allow users to customize the period Siri waits before responding to a user
- Voice Control Spelling Mode, for dictating words letter-by-letter
- Customizable sound recognition of the sounds in your environment
- New themes and text adjustments in the Books app for a more accessible reading experience
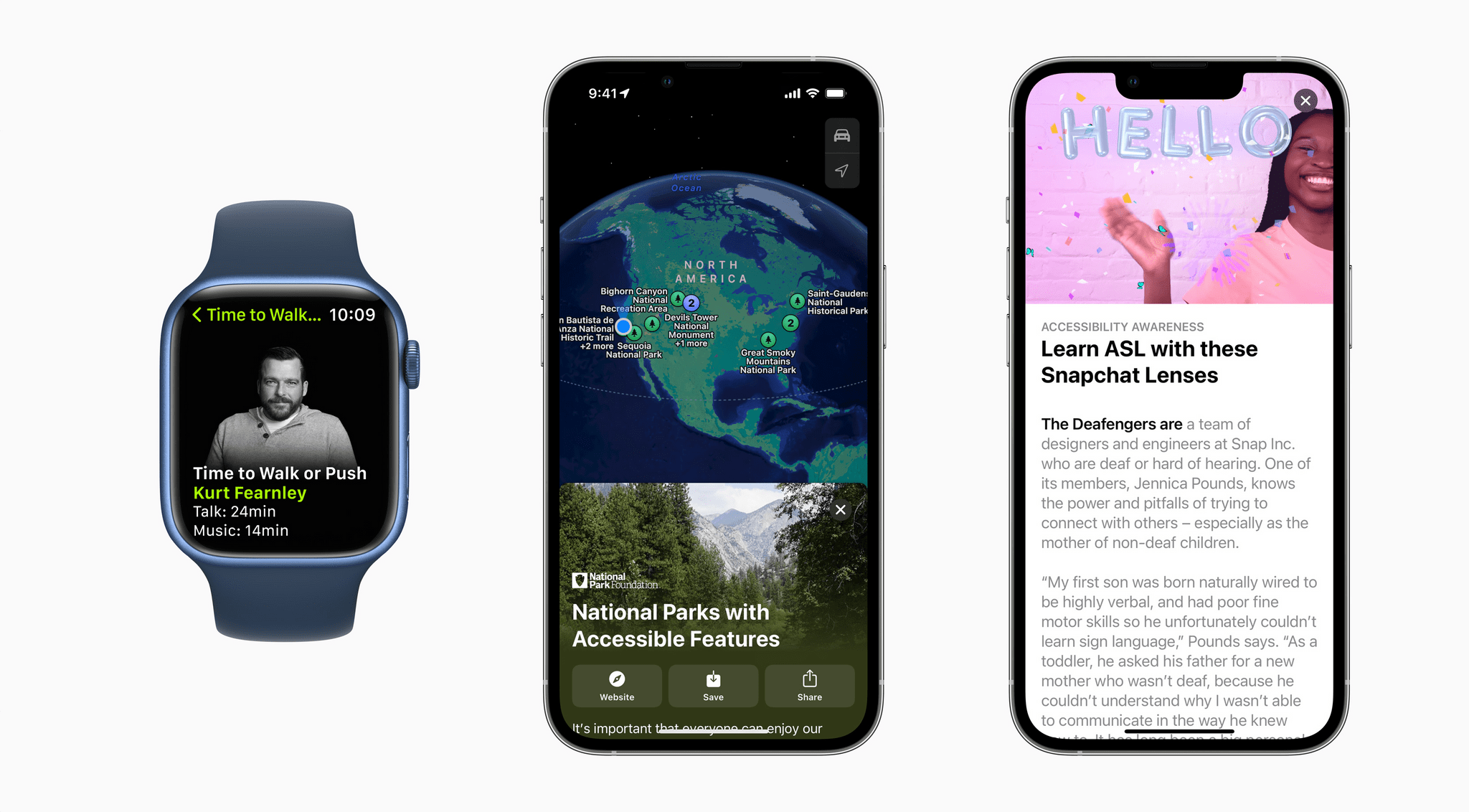
Also, Apple has announced that Global Accessibility Awareness Day is being celebrated with Apple Store sessions, an Accessibility Assistant shortcut in the Shortcuts app, special Fitness+ sessions and Time to Walk or Push episodes, an accessibility-oriented Maps guide, and highlighted content on the App Store and in Apple Books Apple Podcasts, Apple Music and Apple TV.
We’ve seen Apple announce accessibility features coming to future versions of its OSes before, but today’s announcement is unique given the number of features revealed. I’m eager to try these features out. Based on what Apple has said, there seems to be a lot here that will make meaningful impacts on a lot of users’ everyday lives.