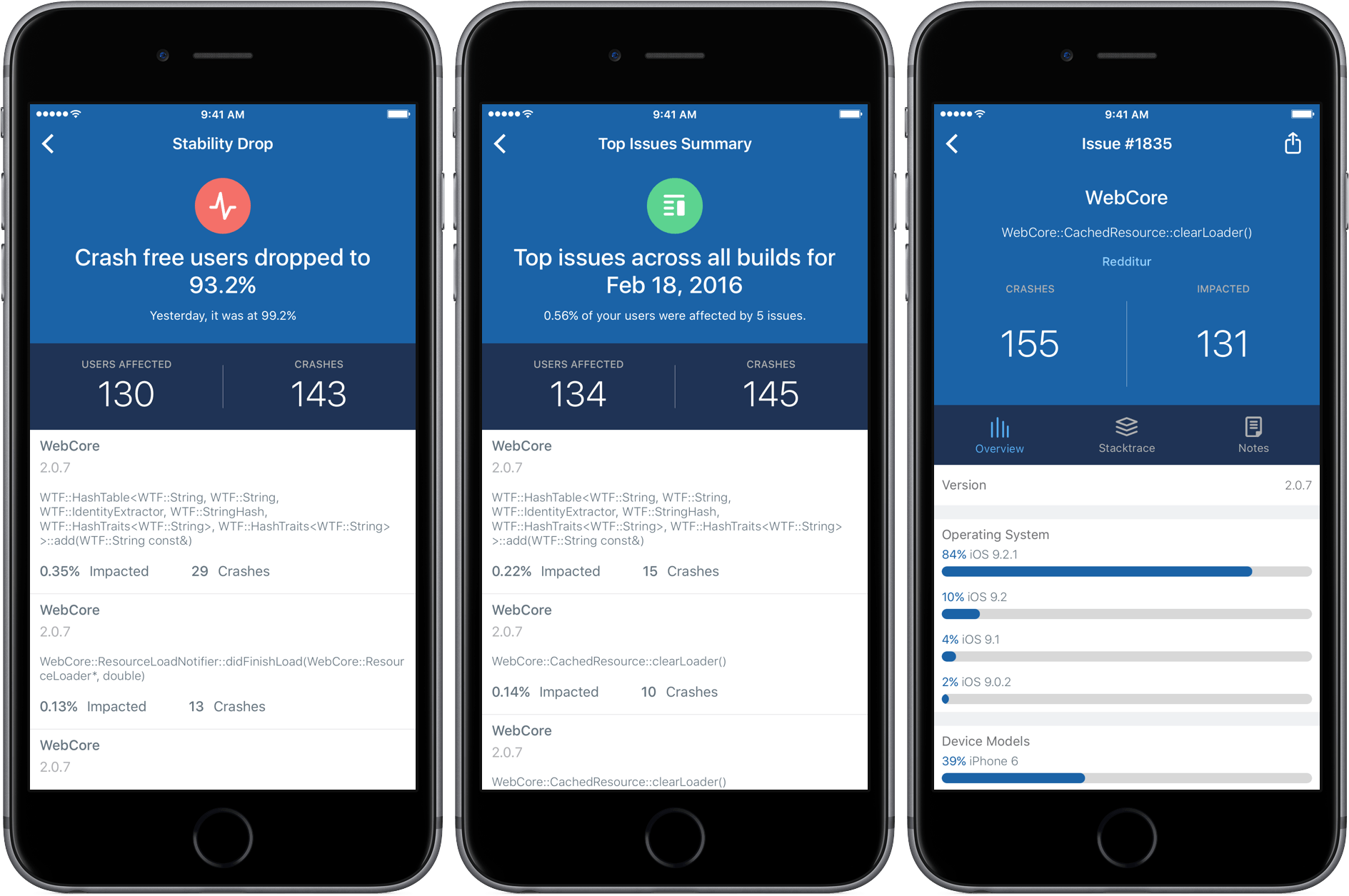
Over the past few years, Twitter has created and acquired an impressive array of mobile developer tools that it offers under the umbrella brand of Fabric. Today, Twitter released an iPhone companion app for Fabric that puts two of its most popular tools in your pocket – analytics and crash reporting. I have been testing Fabric, the iOS app, with two iOS apps provided by Twitter for the last few days and I’m impressed with its ability to sift through, organize, and display large quantities of data in an effective and meaningful way on an iPhone.
Twitter’s Fabric App Brings Real-Time Analytics and Crash Reporting to the iPhone
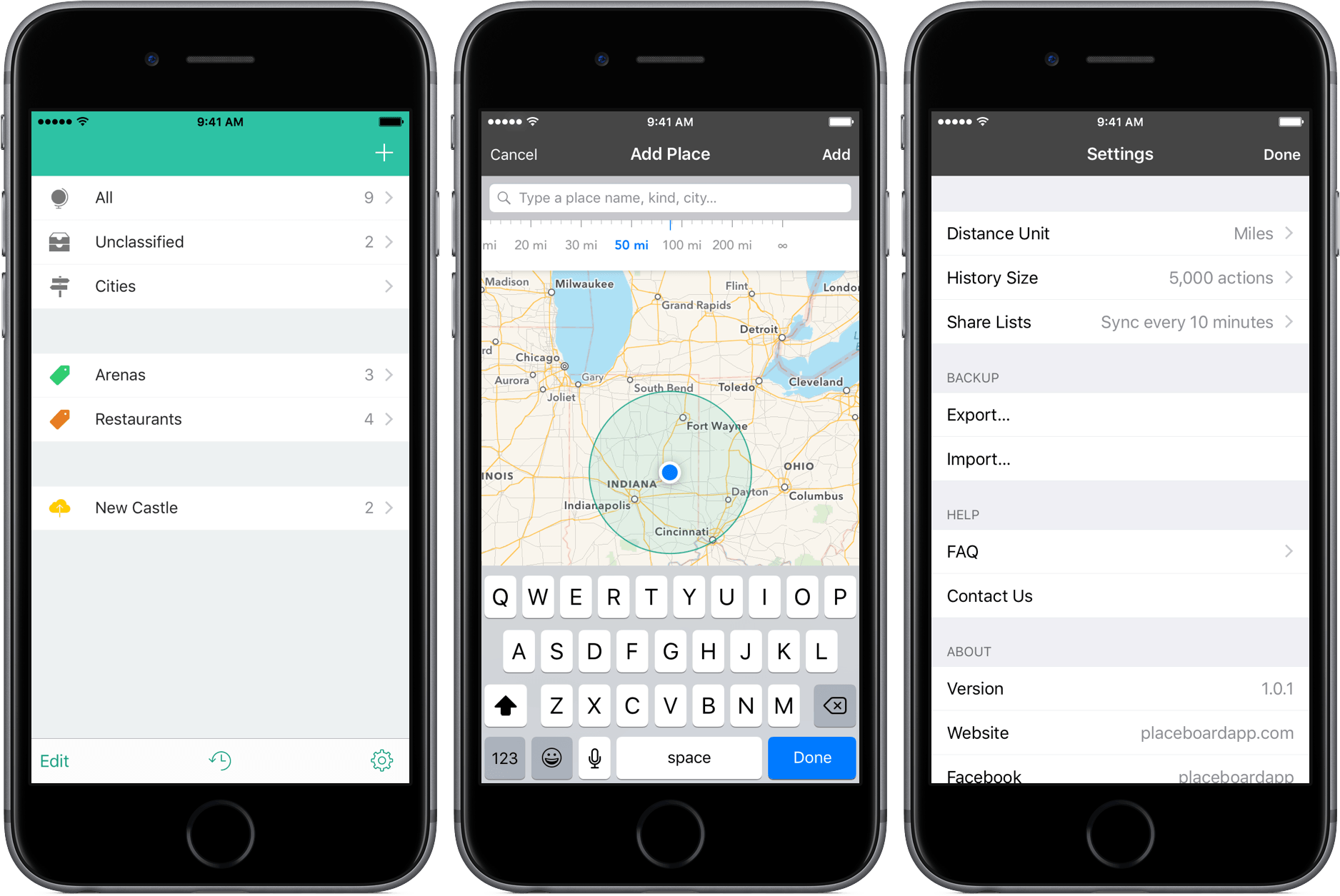
Placeboard: Your Favorite Places in One Location
Among my many bad habits is forgetting to keep frequently-needed information in a convenient place. Whether it’s a phone number or the address of one of my favorite restaurants, I can’t seem to develop a method for storing data I need.
Placeboard is an app that could change that. It’s a storage system for your favorite locations and, with a few smart features, is a great one, too.
A Cautionary Tale About Contacts and Backups
On episode 306 of Mac Power Users, David and Katie talked about contacts on OS X and iOS, including a discussion of Interact, which sounds pretty much like the app that Apple should have built for contacts on iOS. They also mentioned Contacts Cleaner which I consider an indispensable tool for managing contacts on OS X.
However, there are a few details about backing up and restoring contacts that I wanted to add. And by “details” I mean “war stories” and by “war stories” I mean “let me tell you how I got these scars.”
Apple Pencil and Navigation in iOS 9.3 Beta→
Serenity Caldwell, writing for iMore on an Apple Pencil regression in the iOS 9.3 beta:
Unfortunately, whether by bug or intentional design, the Pencil’s navigational prowess appears to have vanished in the iOS 9.3 public betas. With 9.3, you can no longer scroll or manipulate text; the only places the Pencil works are on canvas or when pressing digital buttons.
Normally, I don’t write about beta bugs and features, because it’s a beta: There are always bugs, and features change. But this functionality is important enough that I wanted to talk about it before Apple submits its final 9.3 release. It could be a bug, yes: But several betas in, we’ve seen fixes for Smart Connector keyboards and new features, and the Pencil remains crippled. Which makes me think, more and more, that this is a conscious decision on the part of Apple’s engineering team. (I did reach out to the company about the issue, and will update if and when I receive a response.)
Like Serenity, I refrained from bringing it up due to the beta nature of iOS 9.3, but, as I mentioned earlier today in my iPad story, this is starting to feel like a conscious decision on Apple’s part.
I think it would be a mistake to remove general Pencil navigation features from iOS 9 at this point. While Apple may have not envisioned the Pencil to be used for tasks beyond drawing and sketching, owners of an iPad Pro have gotten used to the functionality four months into owning the device. Using a Pencil to scroll lists and interact with menus has serious benefits for people with RSI problems, and, I have to say, it’s just convenient if you don’t want to switch back and forth between touch and Pencil all the time.
I hope that Apple will listen and restore the full Pencil functionality as seen in iOS 9.2 when the final version of iOS 9.3 ships.
Working on the iPad: One Year Later, Still My Favorite Computer
Four years ago, I struggled to move from a Mac to an iPad. Today, I only have to open my MacBook once a week. And I wish I didn’t have to.
In February 2015, after years of experiments and workarounds, I shared the story of how the iPad Air 2 became my primary computer. The article, while unsurprising for MacStories readers who had been following my iPad coverage since 2012, marked an important milestone in my journey towards being Mac-free.
As I wrote last year:
Three years ago, as I was undergoing cancer treatments, I found myself in the position of being unable to get work done with a Mac on a daily basis because I wasn’t always home, at my desk. I was hospitalized for several weeks or had to spend entire days waiting to talk to doctors. I couldn’t write or manage MacStories because I couldn’t do those tasks on my iPhone and I couldn’t take my MacBook with me. I’d often go weeks without posting anything to the website – not even a short link – because I couldn’t do it from my bed. I began experimenting with the iPad as a device to work from anywhere and, slowly but steadily, I came up with ways to speed up my workflow and get things done on iOS. I promised myself I’d never let a desk set my work schedule or performance anymore.
Being tied to a desktop computer isn’t an option for me. No matter what life has in store for the future, I have to be ready to work from anywhere. I have to consider the possibility that I won’t always be okay, working from the comfort of my living room. That means having a computer that can follow me anywhere, with a screen big enough to type on, and a higher degree of portability than a MacBook. That means using an iPad. That means iOS.
The past 12 months have cemented this vision and raised new questions. But, more importantly, the iPad and iOS 9 have been essential to launching a project I’ve been working on for years.
At this point, I can’t imagine using a computer that isn’t an iPad anymore.
Apple, FBI, and iPhone Security: A Roundup of News and Links
Apple made headlines around the world last week when Tim Cook announced, in an open letter to their customers, that Apple would oppose a court order requiring it to circumvent iOS security features. Since then, new developments in the story have broken and many have contributed with explanations of why the outcome of this battle between Apple and the FBI is significant.
Our relative silence on this topic at MacStories is not because we don’t think this story is important. To the contrary, we believe it is incredibly important and we applaud the principled stand that Cook’s Apple has decided to make. But we are hesitant to wade into this important debate, which can be incredibly technical, when there are far smarter minds out there who better deserve your time and attention.
To that end, we’ve compiled a list of useful news articles, opinion pieces, and other resources that we believe are worth a few minutes of your time.
Apple Issues Fix to Restore iPhones Disabled by Error 53→
Earlier today, Apple issued a patched version of iOS 9.2.1 that restores iPhones disabled by Error 53, which gained notoriety a couple of weeks ago after a report by The Guardian.
Today, Apple is issuing an updated version of iOS 9.2.1 for users that update their iPhones via iTunes only. This update will restore phones ‘bricked’ or disabled by Error 53 and will prevent future iPhones that have had their home button (or the cable) replaced by third party repair centers from being disabled. Note that this is a patched version of iOS 9.2.1, previously issued, not a brand new version of iOS.
As I hoped, Apple has fixed iOS’ behavior so that iPhones will no longer be bricked by Error 53. From the company’s statement to TechCrunch:
We apologize for any inconvenience, this was designed to be a factory test and was not intended to affect customers. Customers who paid for an out-of-warranty replacement of their device based on this issue should contact AppleCare about a reimbursement.
Understanding Night Shift’s Impact on Accessibility
To my knowledge, the release of Night Shift in iOS 9.3 is only the second time in recent history Apple has updated iOS to include a change or feature that has potential accessibility ramifications. The other occurrence, in my mind, was iOS 7.1 beta 2, released in 2013. In it, Apple added a Button Shapes option to Accessibility as a way to assuage users who have trouble distinguishing an actionable button from a text label. Generally, however, any significant additions or changes to the Accessibility feature set comes included with a major new version of iOS. That is to say, the version Craig Federighi talks about at the annual WWDC keynote.
Before getting into Night Shift’s accessibility merit, it’s worth examining why it exists. The impetus for Night Shift is better sleep. Apple explains in its marketing material for iOS 9.3 that a person’s circadian rhythm can be disrupted by the “bright blue light” emitted from an iPhone or iPad’s screen, making it difficult to fall asleep. What Night Shift does to combat this, according to Apple, is “use your iOS device’s clock and geolocation to determine when it’s sunset in your location.” After gathering that data, the software then “automatically shifts the colors in your display to the warmer end of the spectrum.” The end result is a display that’s easier on the eyes, thus hopefully making it easier to fall asleep. (The display settings will revert to normal in the morning. There’s an option to schedule Night Shift as well.) For more on why Night Shift is important and how it works, iMore has posted a good explainer on the feature.
Bloomberg’s Profile of Apple’s Chief Chipmaker, Johny Srouji→
Good profile by Brad Stone, Adam Satariano, and Gwen Ackerman, with some interesting details about the iPad Pro’s original schedule and Srouji’s background.
A little over a year ago, Apple had a problem: The iPad Pro was behind schedule. Elements of the hardware, software, and accompanying stylus weren’t going to be ready for a release in the spring. Chief Executive Officer Tim Cook and his top lieutenants had to delay the unveiling until the fall. That gave most of Apple’s engineers more time. It gave a little-known executive named Johny Srouji much less.
Srouji is the senior vice president for hardware technologies at Apple. He runs the division that makes processor chips, the silicon brains inside the iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, and Apple TV. The original plan was to introduce the iPad Pro with Apple’s tablet chip, the A8X, the same processor that powered the iPad Air 2, introduced in 2014. But delaying until fall meant that the Pro would make its debut alongside the iPhone 6s, which was going to use a newer, faster phone chip called the A9.