Here are today’s @MacStoriesDeals on iOS, Mac, and Mac App Store apps that are on sale for a limited time, so get them before they end!
#MacStoriesDeals - Tuesday
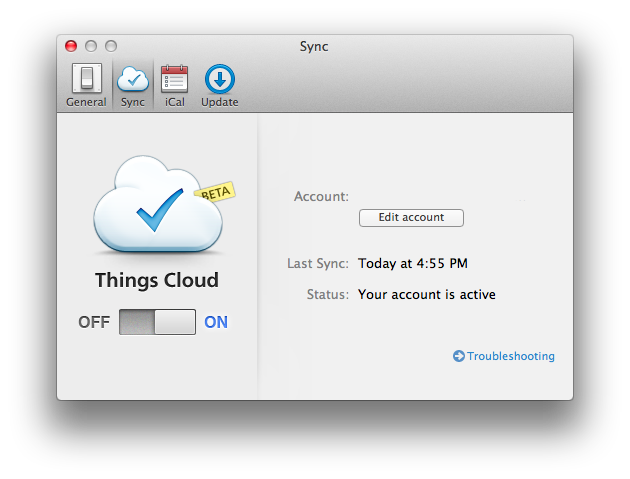
Things Cloud Goes Public Beta
Originally announced last year, Things Cloud, a cloud syncing platform for Cultured Code’s Things GTD app, is now available as public beta. Available on the Mac and iOS, Things is one of the most popular applications to manage todos and projects, and the app even won an Apple Design Award for its ease of use and simplicity. Cultured Code, however, has been heavily criticized by its user base over the years for the lack of a cloud syncing solution that would allow Things for iOS to stay up to date with Things for Mac; the criticism was also exacerbated by the fact that other GTD apps for the Mac and iOS, namely OmniFocus and Firetask, implemented working, reliable cloud databases in a relatively short period of time, whilst also adding new functionalities to their apps for paying customers.
We’ve had incredible feedback from our users, telling us that Things Cloud is proving to be both fast and stable. Some of our users have adopted the beta entirely and created exceptionally large databases. In the coming weeks we are going to work out some kinks and performance bottlenecks related to such large databases. This is an important final step towards enabling the import of existing data. Once the import feature is ready, we’ll post another update.
Whilst we’ll leave our thoughts for a review once the software leaves beta, it’s important to note that Cultured Code has always claimed its syncing solution would require more work (thus additional time to be implemented) because of a different technology being used to effortlessly push tasks and data across devices. For what it’s worth, I have been able to test Things Cloud, and its sync process was indeed pretty fast both on WiFi and 3G. I’ll save further considerations and tests for a proper review.
To enable Things Cloud, you can head over Cultured Code’s website and download the Mac beta. Cloud syncing can also be enabled by downloading the public version of Things for iOS, following the instructions provided on Cultured Code’s website.
Screens 2.0 Review
I’ve always been a huge fan of Edovia’s take on VNC, Screens. Originally released in late 2010 for the iPad, Screens was also ported to the iPhone and later the Mac, allowing iOS and OS X users to connect to remote machines using standard VNC protocols (Lion logins are also supported by Screens), as well as Edovia’s own ScreensConnect utility to assign a unique hostname to computers behind networks that allow for outside access. To get an overview of Screens, you can take a look at some of your previous coverage.
Today Edovia is releasing a series of major updates to Screens for iOS and Mac, as well as ScreensConnect, which is now available at screensconnect.com to create a unique Screens ID for your Mac or Windows machine. I have been able to test the new Screens suite prior to its App Store release, and it’s still my favorite utility to quickly access my remote Mac mini, iMac, or MacBooks (Air and Pro) on my local office network. With its touch-driven UI, ease of use, and wide availability across devices (Mac, iPhone, and iPad for the Screens client; Windows and OS X for the desktop ScreensConnect utility), Screens is one of the most accessible VNC apps available on the App Store.
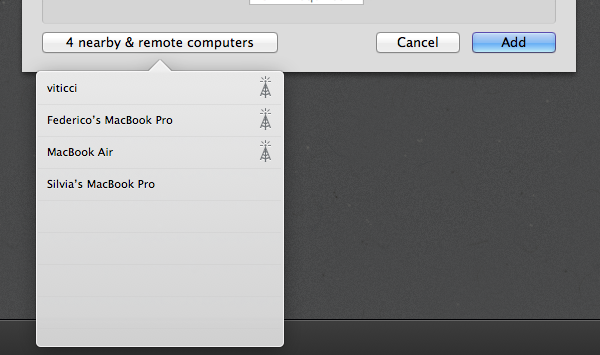
Since its release, I’ve always liked two things about Screens: touch controls and zero configuration. Once you download Screens, you’ll be able to search for computers that are advertising their screen sharing capabilities on a local network (on a Mac, make sure Screen Sharing is active under System Preferences -> Sharing), or add a machine that’s been configured to be reached using ScreensConnect. In the “Nearby & remote computers” window (a popover on the Mac), you’ll see computers from your local network, as well as those with an antenna icon next to them, indicating that they accept remote connections through ScreensConnect. The beauty of ScreensConnect, which is a free utility, is that it should make your computer accessible from outside your local network with literally no configuration, as the software takes care of (most) router settings and establishes a secure connection between a remote computer and Screens. As explained from the app’s Help section:
We could bore you with technical mumbo-jumbo but in a nutshell, Screens Connect monitors network changes, configures your router and sends this information on our server through a SSL encrypted connection so that Screens knows were your computer is and connect to it.
A note on ScreensConnect: whilst most modern routers support UPnP and NAT-PMP (required by Screens’ remote connection), some do not, so make sure you have a compatible model before considering Edovia’s Screens for its ScreensConnect functionality alone. I, for one, got ScreensConnect working just fine with my Fastweb connection in Italy (through Apple’s AirPort Extreme), as well as Telecom’s Alice (through an AirPort Express). Performance, as usual, depends on your Internet connection, so don’t expect ScreensConnect to magically improve speeds – there’s only so much smart connection scaling (from millions of colors to hundreds) can do.
Screens 2.0 comes with a new UI. Gone is the wooden texture of the previous versions, leaving room for a darker, more elegant background that will surely make your computer’s desktops pop. Whilst the change in visual presentation is welcome, much more functional is iCloud integration in version 2.0, which now allows you to keep your stored screens in sync across devices – and it’s just not “sync”, I was able to create a new screen on the Mac app, wait a few seconds, and see it coming up automatically on the iPhone and iPad, which were running Screens 2.0. Support for iCloud is fairly impressive and a godsend, because, honestly, adding the same screens over and over on multiple devices wasn’t really a great experience.
Alongside bug fixes, improved security and performances, and better support for wake-on-lan, Screens 2.0 comes with some additional new features. When controlling a computer, for example, Screens now displays a unified bottom toolbar that collects a series of shortcuts – including two types of keyboards, and an action button to grab a screenshot of the remote desktop (a new feature), disconnect, and open the Settings. On the iPad, this toolbar can be configured to become a swipe gesture area whilst in landscape mode, allowing you to associate a variety of commands to left or right swipes. The same app/Mac/window shortcuts can be configured with three and four finger gestures to perform directly on screen, and the selection here is very rich – for instance, you’ll be able to set up shortcuts to send the contents of your clipboard, or launch Mission Control.
Also new in Screens 2.0: you can reorganize screens in grid mode on the iPad, you can send the remote screen to an Apple TV using AirPlay Mirroring, and SSH Keys are now supported for SSH Tunneling. On the Mac, you won’t obviously get the iOS version’s custom keyboards and gesture support, but Screens 2.0 will support iCloud and auto-resume for ongoing connections.
With a new UI, better handling of remote connections, gestures, iCloud support, and a very intuitive touch-based VNC control system, Screens 2.0 is a fantastic update. ScreensConnect works as advertised, the iPad app benefits from the screen real-estate, and, overall, the app is very easy to use and configure. Screens, however, doesn’t come cheap, as the iOS app (universal) and Mac app will set you back $50 when combined. If you’re willing to pay for quality software and believe Screens’ feature set is right for you (make sure your router can work with ScreensConnect!), I’d personally recommend starting with Screens 2.0 for iOS today. Read more
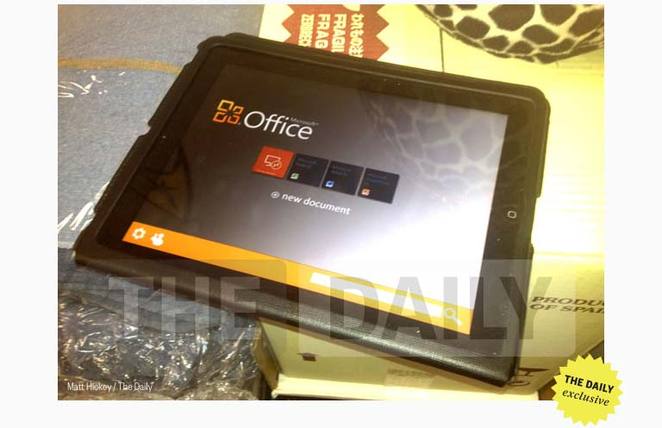
Microsoft Office For iPad Coming Within Weeks? [Updated]
Microsoft’s Office Suite could be launching on the iPad App Store within weeks according to a new report in The Daily. Originally rumoured in November of last year by The Daily, Matt Hickey today says that the design team has “wrapped up the project” but an exact launch date was not known.
Hickey claims to have had a brief hands-on with a working prototype of the Office Suite app and notes that whilst the UI is similar to OneNote for iPad, it has hints of Metro. He notes that Word, Excel and PowerPoint files can be created and edited either locally on the iPad or online (presumably using Microsoft’s SkyDrive cloud service).
According to his sources, OneNote will also receive an update soon to reflect the Metro design. Those same sources also noted that no Android version was in the works.
[The Daily via The Next Web]
Jump the break to view all updates to this story.
China Telecom To Offer The iPhone 4S From March 9th
Starting from March 9th, China Telecom customers will be able to purchase the iPhone 4S. It comes about two months after China Unicom first offered the iPhone 4S in China.
Unlike China Unicom (the second largest carrier after China Mobile), the smaller China Telecom uses the CDMA technology. Though because the iPhone 4S has support for both CDMA and GSM networks, China Telecom will be selling the same hardware that customers on China Unicom and customers elsewhere across the world purchase.
iPhone has been available on China Unicom which has 37 million 3G users. New distribution through China Telecom adds 33 million 3G subs.
— Horace Dediu (@asymco) February 21, 2012
[via The Verge]
iPad 3 Variables
With the (rumored) next-generation iPad approaching its (rumored) announcement on March 7th, I thought it would be interesting to collect some of the predictions we’ve made thus far based on the rumors and oft-quoted “inside reports” we have heard until today.
Unlike most Apple product launches, like, say, the iPhone 4S in October, there seems to be a certain degree of certainty in what the device is going to look like and the hardware changes it’ll feature when compared to the existing iPad. Thanks to various parts that have surfaced from China, several mentions by Daring Fireball’s John Gruber, and a general assumption that “it’s about time”, it appears the iPad 3 is going to feature a high-resolution, 2048 x 1536 Retina Display. Just like the jump from iPhone 3G-era displays to the iPhone 4, a Retina iPad (which John Gruber has been predicting since 2011) would allow for crisper graphics on screen and a better reading experience thanks to the increased number of pixels per inch.
Reported in just about any recent rumor on the iPad 3, the Retina Display has become the marquee addition those who follow Apple rumors expect to see in the next-gen device. As we’ve seen with our previous coverage, however, there are other hardware changes that Apple could bring to the iPad 3, namely better cameras, faster processor, and LTE connectivity.
In the past months, I have seen reactions from people who have followed the iPad 3 rumors typically split in two categories:
Theory #1: iPad 3 has Retina Display, new cameras, LTE, new A6 processor.
Theory #2: iPad 3 has Retina Display, slightly improved cameras, faster A5 processor.
The two theories imply that the new iPad is going to be a major revision with dramatically faster CPU and graphics to power the Retina Display plus LTE connectivity, or a speed-bump of the existing iPad with the addition of a Retina Display, but no LTE, dramatically faster processor, or iPhone-class cameras. Both are based on a series of rumors, patterns, and facts to be considered. Read more
Growl, Mountain Lion, And “Getting Sherlocked”
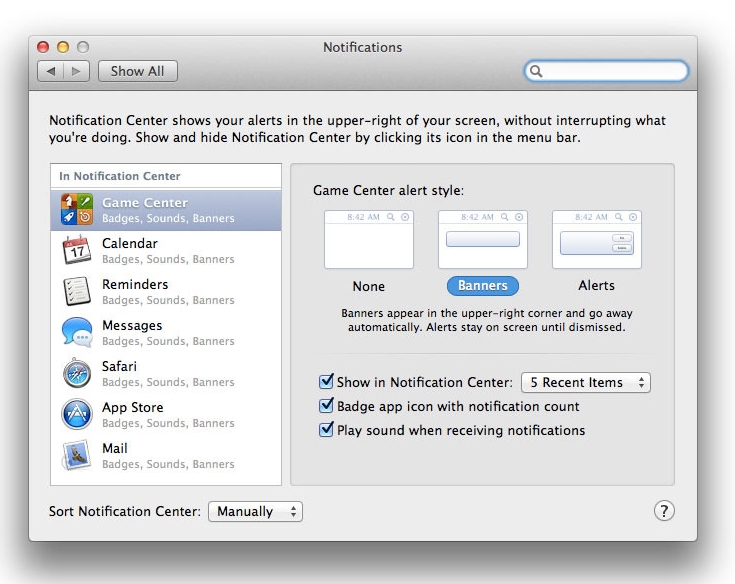
Last week Apple revealed its new Mac operating system, Mountain Lion, due out for this summer. While not a complete overhaul, 10.8 is a polished update that adds many similar functionalities from iOS 5. Among these changes, and one of the most important pieces, is Notification Center. As the name suggests, it is basically Notification Center ported from iOS, running at a system level on Mountain Lion. Besides having the same UI elements we see on our iPads and iPhones everyday, it also has a badge mode much like Growl, our favorite open source notification system for OS X. It’d be fair to say that almost every OS X die-hard uses Growl, as it’s very customizable with function and appearance. Last year, the Growl team overhauled the app and submitted it to the Mac App Store, where it quickly became one of the most popular utilities in the Top Paid charts.
Following Apple’s announcement, some people have said Notification Center will create a problem for Growl, as Apple’s own solution could hurt Growl by replacing its functionality on OS X. Now, as far as I know, Mountain Lion’s Notification Center will only work with Mac App Store apps, so Growl could still have a place for third-party apps that are installed outside of Apple’s storefront, as allowed by Gatekeeper.
Growl doesn’t seem to think Notification Center will immediately hinder installation or usage of their app, either. In a blog post from February 17th, the developers say Growl still has room in OS X to play with. They have listed some points as to how Growl will continue to go forward:
- The developers are investigating options for integrating Growl with Notification Center.
- Growl will work whether your application is from the App Store or not, as long as it supports Growl.
- They’re still on schedule to release Growl 1.4 and 2.0.
- Growl is great for customizable notifications.
- Development of other applications will continue, such as HardwareGrowler, GrowlTunes, and Capster as Mac App Store apps.
The Growl developers are optimistic even though they are going to have to compete with Apple. With Growl 1.4 already in beta testing (with many great improvements) and work on Growl 2.0 underway, I wouldn’t say Growl has been been “Sherlocked” by Apple’s announcement.
As a side note, developer Collect3 released Hiss today, a free app that sends all Growl notifications directly to Mountain Lion’s Notification Center. So, if you have an app that supports Growl, not Notification Center, you’re in luck. This could be the first step in both Growl and Mountain Lion’s Notification Center working together in some way (much like Notification Center hasn’t hurt the extensibility of Boxcar), albeit Connect3 was quoted on The Verge as saying that “(Hiss was) just a result of us being impatient to start seeing Notification Center become useful.”
[image via Macworld]
#MacStoriesDeals - Monday
Here are today’s @MacStoriesDeals on iOS, Mac, and Mac App Store apps that are on sale for a limited time, so get them before they end!
“Creating Flow with OmniFocus” Now Available as Audiobook
The aim of this text then is not just in using the productivity and task management program OmniFocus, but also in getting to the creative space wherever that may be found. The hope is in getting to those things you want to do and enjoy while maintaining the responsibilities that inevitably accrue in life. Be it in work, play, or with family, we are aiming for a relaxed depth of focus and flow.
Originally released in November 2010, Creating Flow with OmniFocus by Kourosh Dini is one of the best resources available to learn more about The OmniGroup’s fantastic GTD software. Specifically aimed at Mac users of OmniFocus, the 555 pages of Dini’s book will take you through the basic concepts of the application, such as Projects and Contexts, to more advanced techniques and workflows that may involve prioritization of your tasks, context management and, overall, finding the right “flow” for your tasks and Getting Things Done system. As a reader of Creating Flow with OmniFocus myself, I’ve always been impressed with the way the author made this book about balancing your own creativity with goals and projects you have to complete in real-life, rather than simply writing a “how to” guide for OmniFocus. Sure, the book has its tutorial-oriented sections with screenshots and tips, but I found the overall “focus” on creating flow and making the system work for you quite liberating.
Creating Flow has been substantially improved since its original release. Kourosh Dini worked hard to bring the book up to speed with the latest refinements introduced in OmniFocus for Mac (now at version 1.9), and today he released an audiobook version that is available on his website. I have been able to listen to a pre-release copy of the audiobook, and it’s a good alternative for those times when you don’t want to sit down with a full copy of the eBook in your Mac or iPad PDF reading app of choice (personally, I like PDF Expert), but still would like to catch up on some great OmniFocus suggestions and discussion. In fact, I would say that the biggest advantage of the audiobook is that, once synced to your iOS device, you’ll be able to quickly navigate between chapters and instantly get to your desired section with just one tap. You’ll lose images and the overall visual style of the eBook (albeit the .zip file comes with a reference of over 300 screenshots), but you’ll gain an improved navigation that makes it easy to skip sections you don’t want to listen to again if you’ve already read the book. In this regard, existing owners of Creating Flow should consider supporting Kourosh again and get the audiobook just to have a refresh on some parts of the original book without having to go through it again.
The audiobook has been narrated by professional voice actor, Bruce Edwards, encompassing nearly 10 hours of listening material. As I wrote in 2010, Creating Flow with OmniFocus is the book every OmniFocus user should read. Now you can listen to it as well with the audiobook available here.