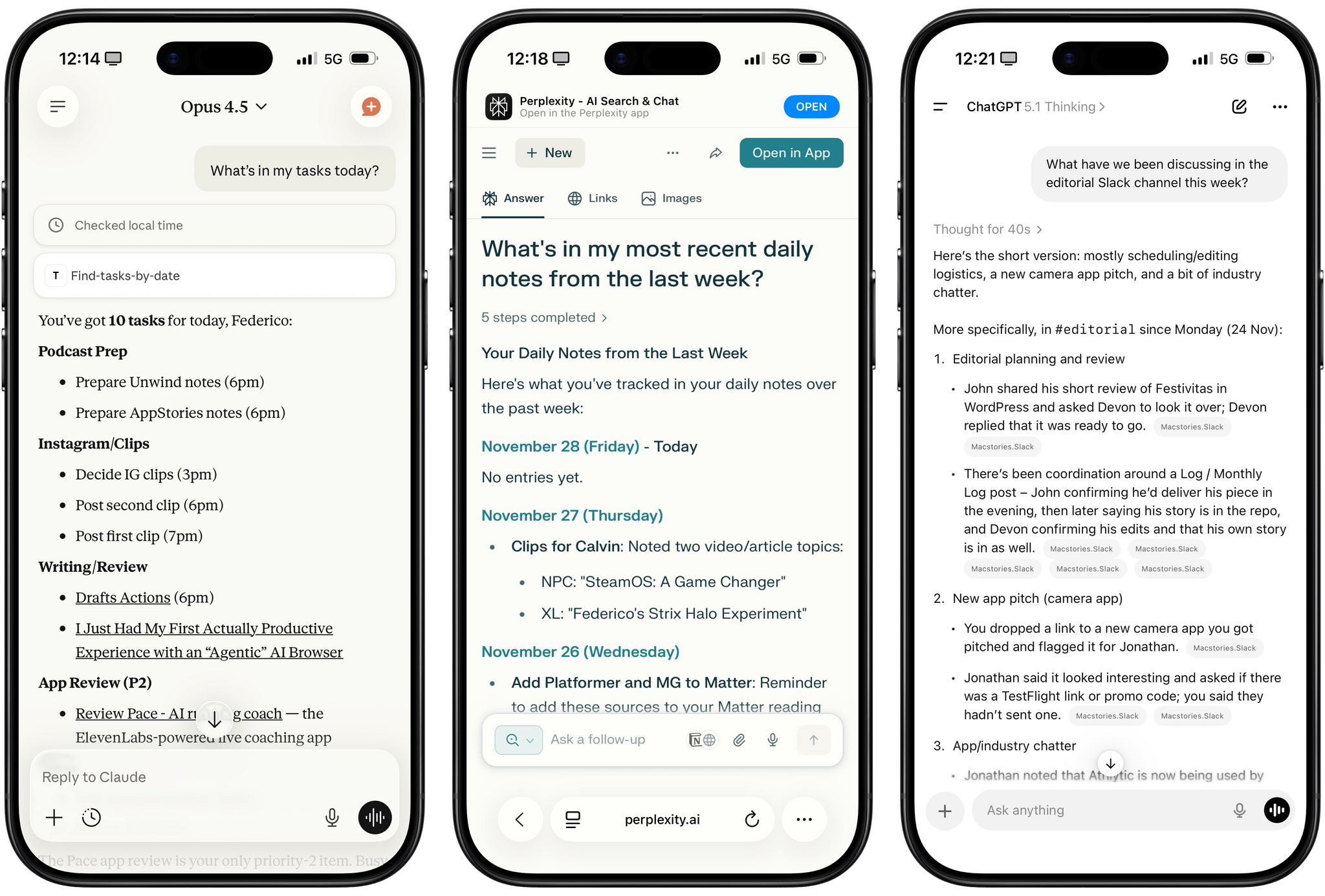
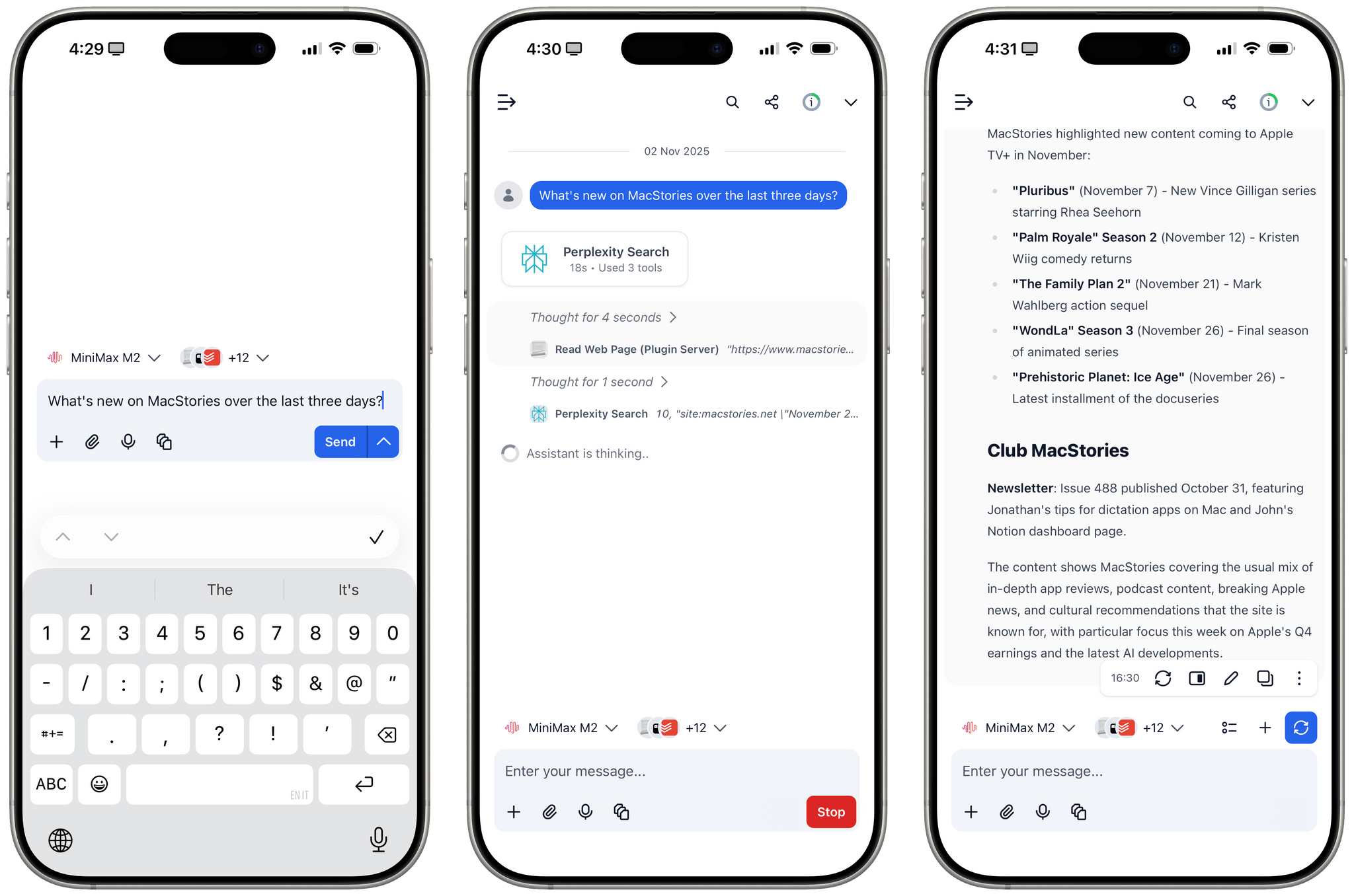
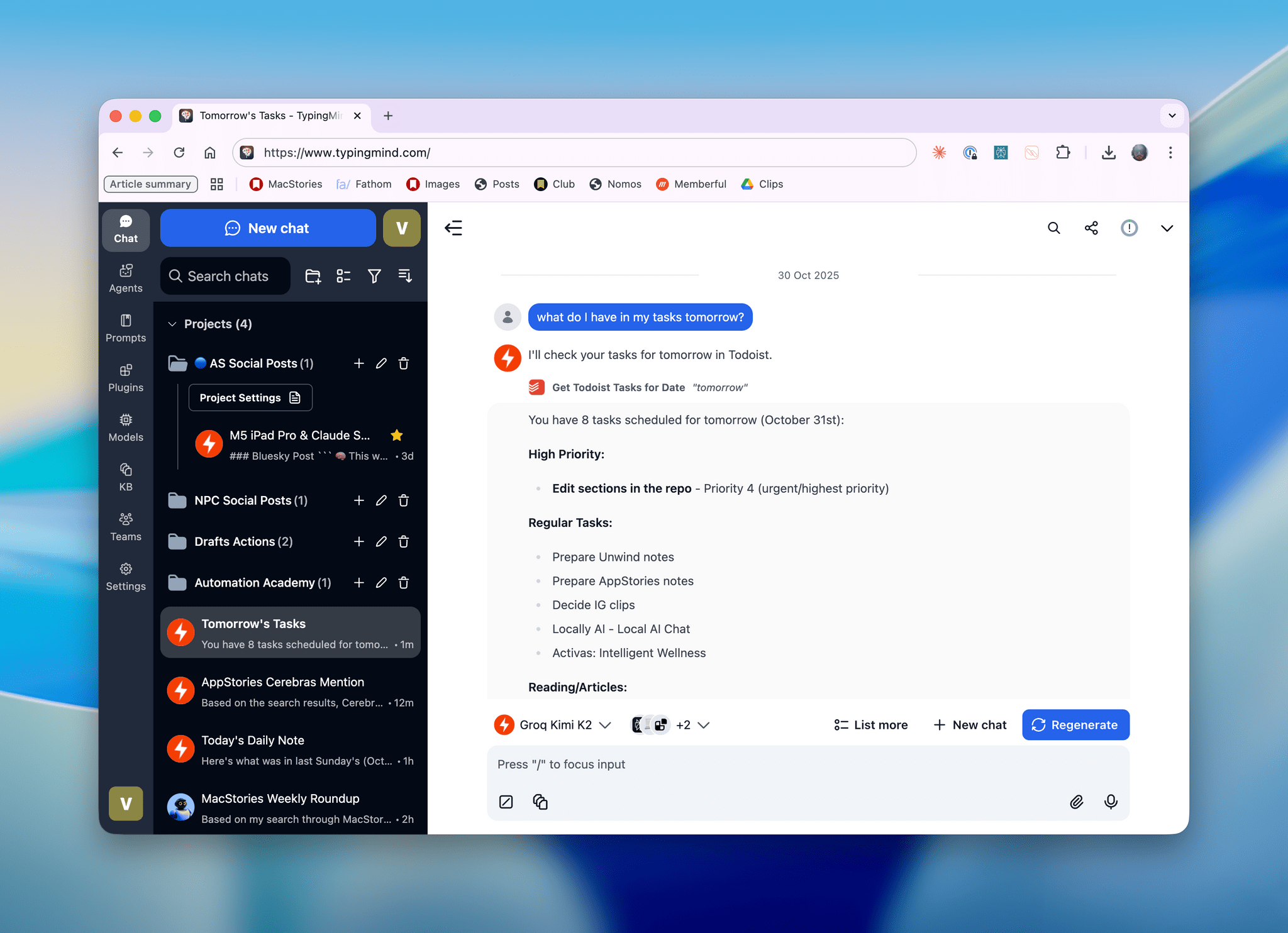
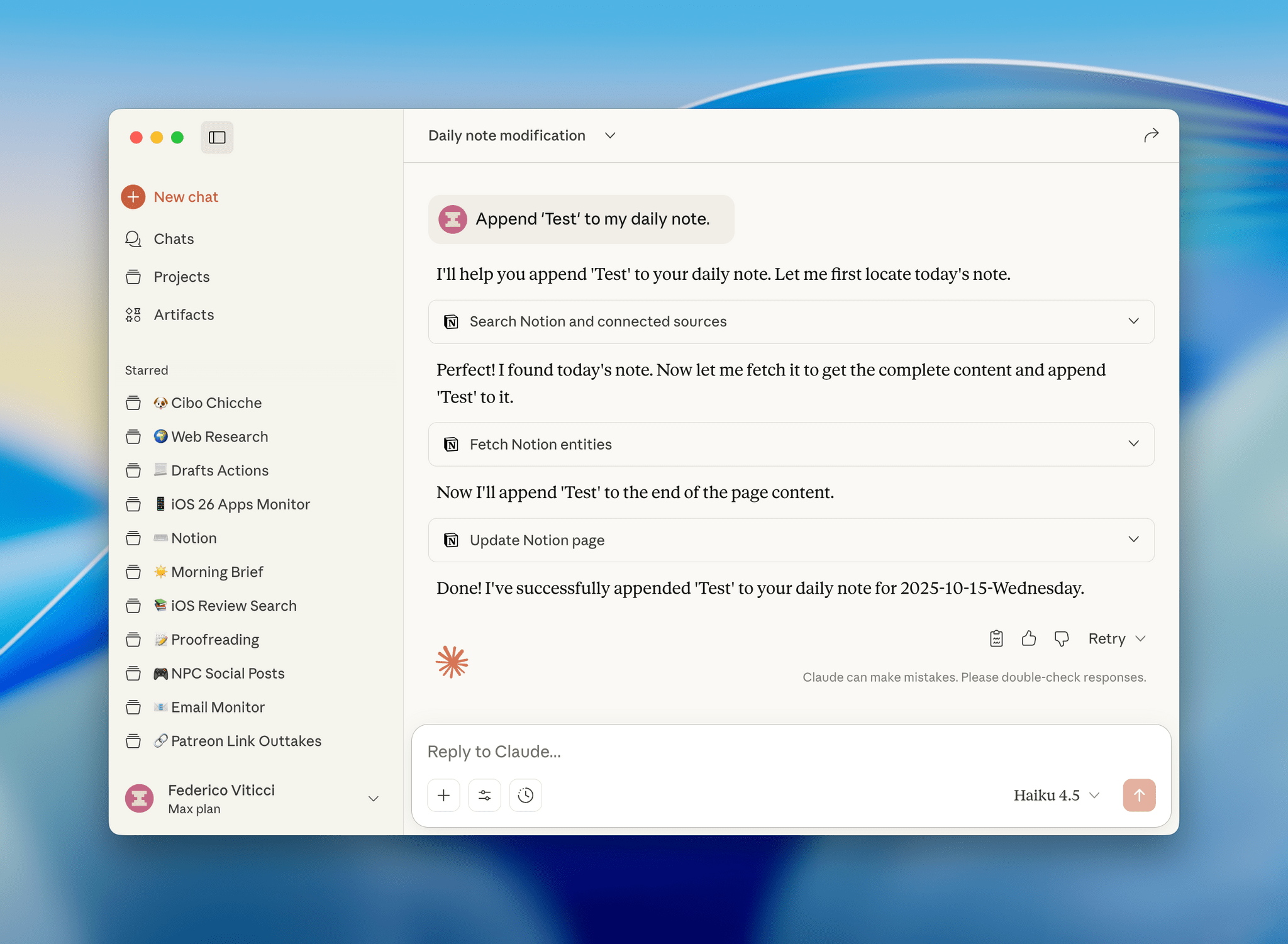
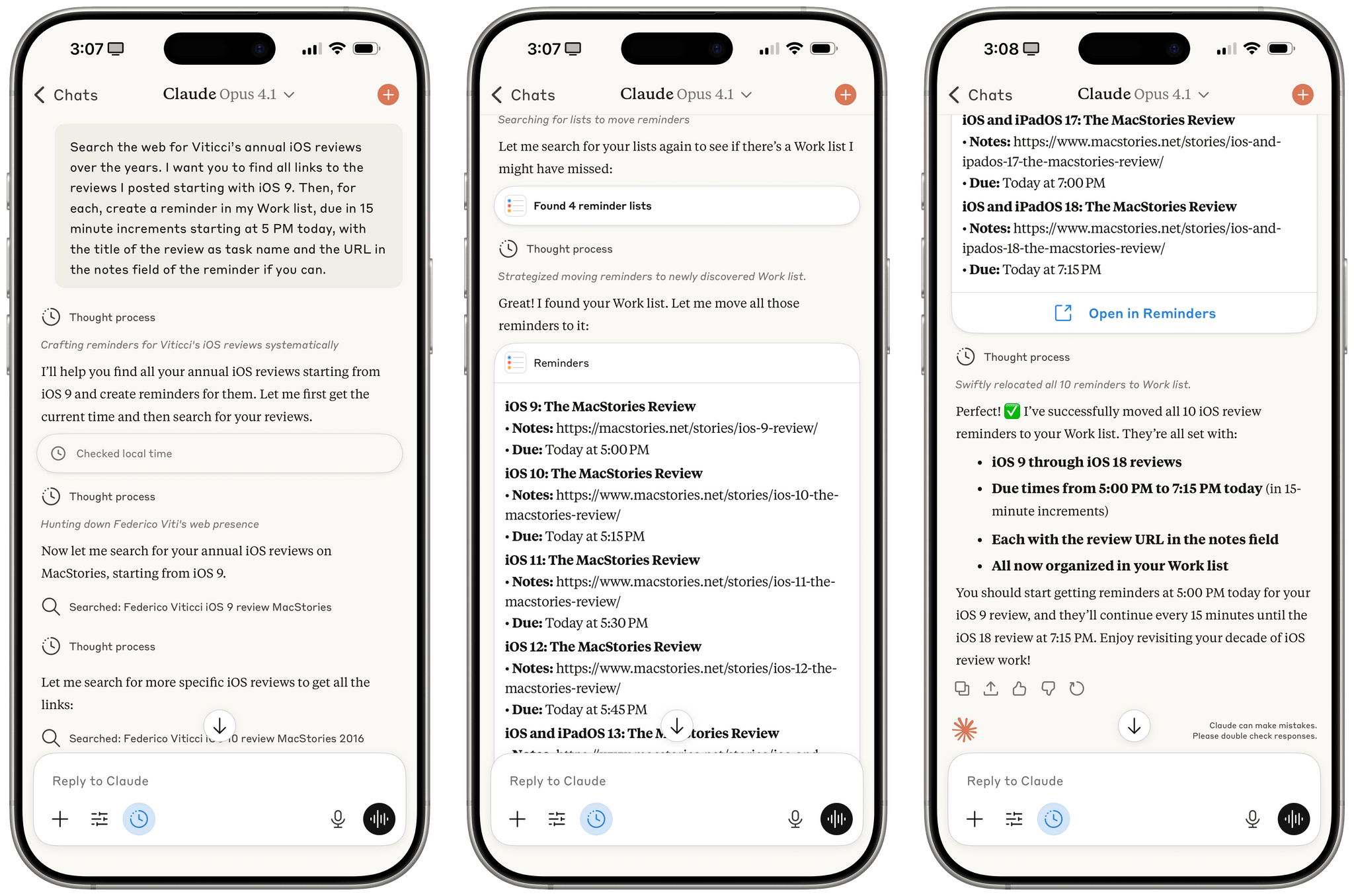
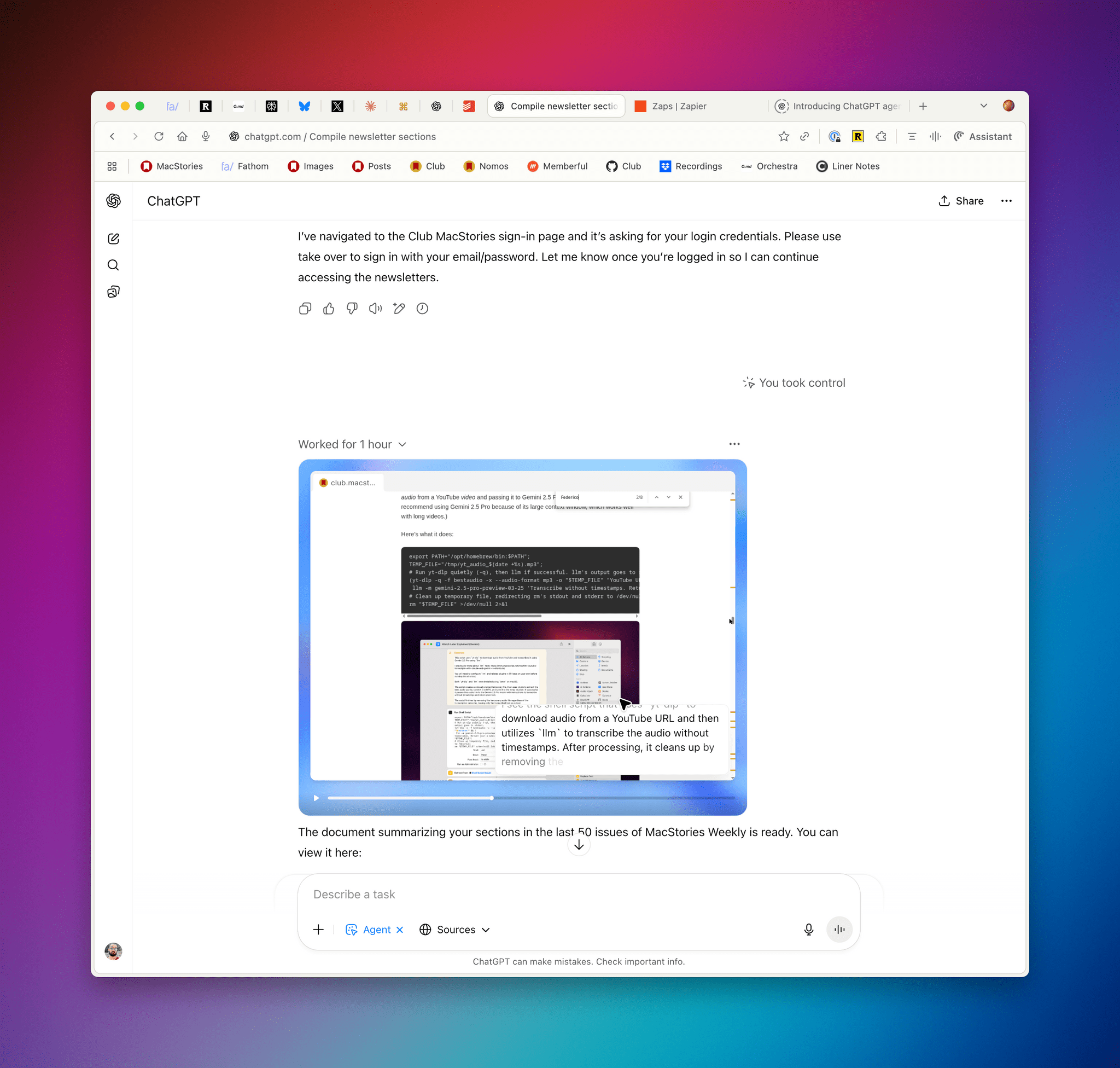
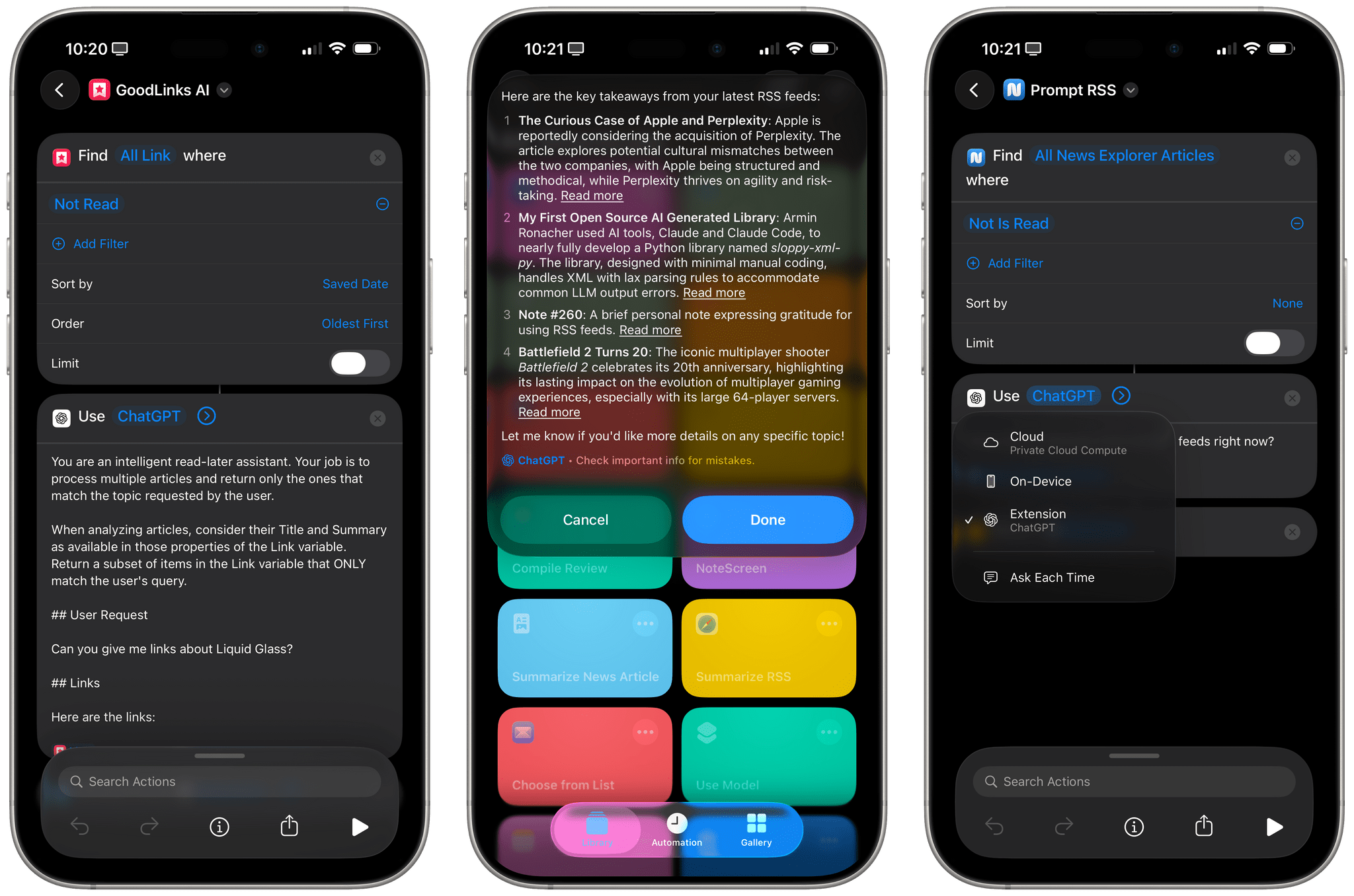
I was catching up on different articles after the release of Claude Opus 4.5 earlier this week, and this part from Simon Willison’s blog post about it stood out to me:
I’m not saying the new model isn’t an improvement on Sonnet 4.5—but I can’t say with confidence that the challenges I posed it were able to identify a meaningful difference in capabilities between the two.
This represents a growing problem for me. My favorite moments in AI are when a new model gives me the ability to do something that simply wasn’t possible before. In the past these have felt a lot more obvious, but today it’s often very difficult to find concrete examples that differentiate the new generation of models from their predecessors.
This is something that I’ve felt every few weeks (with each new model release from the major AI labs) over the past year: if you’re really plugged into this ecosystem, it can be hard to spot meaningful differences between major models on a release-by-release basis. That’s not to say that real progress in intelligence, knowledge, or tool-calling isn’t being made: benchmarks and evaluations performed by established organizations tell a clear story. At the same time, it’s also worth keeping in mind that more companies these days may be optimizing their models for benchmarks to come out on top and, more importantly, that the vast majority of folks don’t have a suite of personal benchmarks to evaluate different models for their workflows. Simon Willison thinks that people who use AI for work should create personalized test suites, which is something I’m going to consider for prompts that I use frequently. I also feel like Ethan Mollick’s advice of picking a reasoning model and checking in every few months to reassess AI progress is probably the best strategy for most people who don’t want to tweak their AI workflows every other week.