One of the greatest frustrations I’ve had with Claude Code is feeling tied to my desk or being stuck in a macOS Screen Sharing window. Claude Code’s new Remote Control feature, which was introduced late yesterday, promises to eliminate that frustration entirely. Here’s how it works.
Posts tagged with "artificial intelligence"
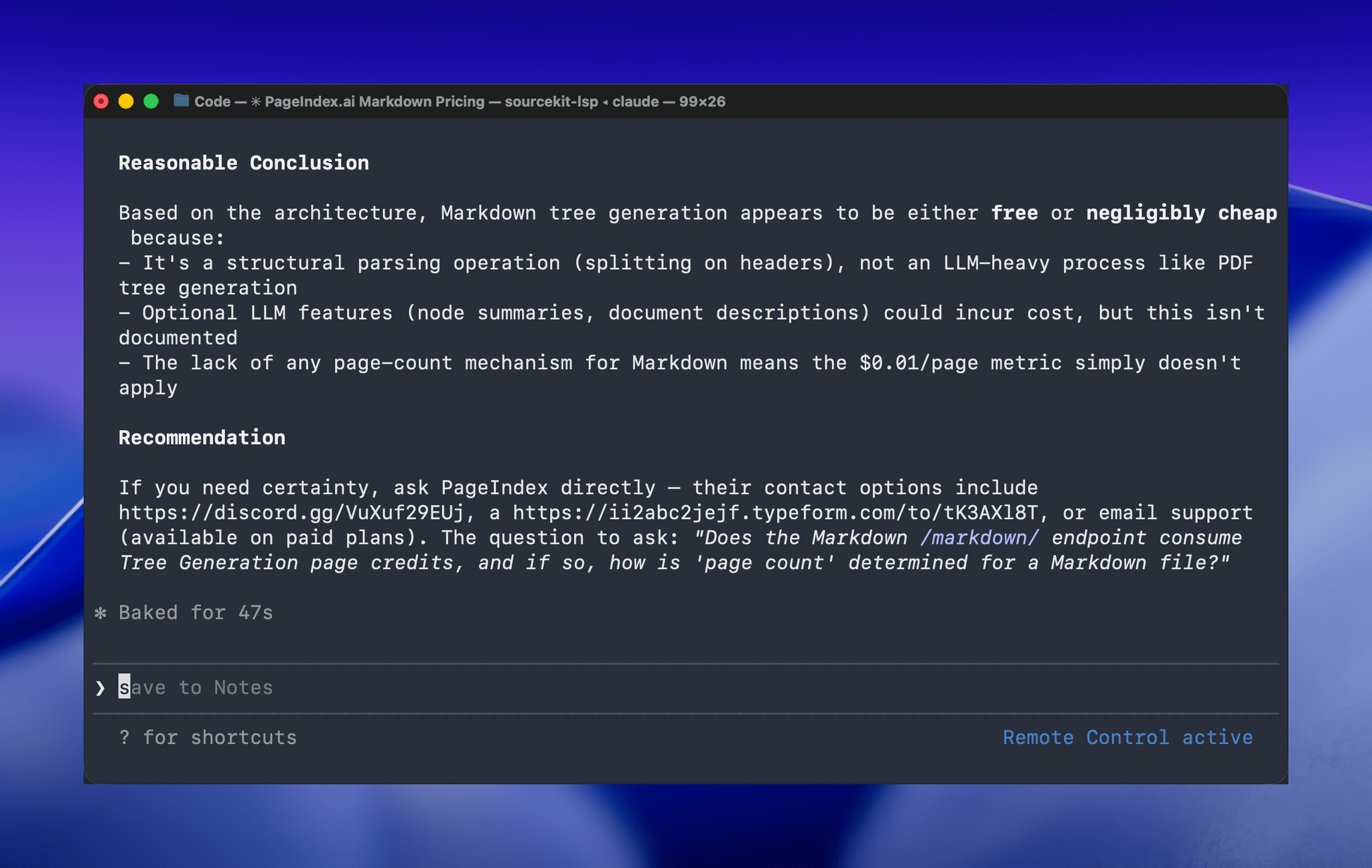
Hands-On with Claude Code Remote Control
OpenClaw Showed Me What the Future of Personal AI Assistants Looks Like
Update, February 6: I’ve published an in-depth guide with advanced tips for secure credentials, memory management, automations, and proactive work with OpenClaw for our Club members here.
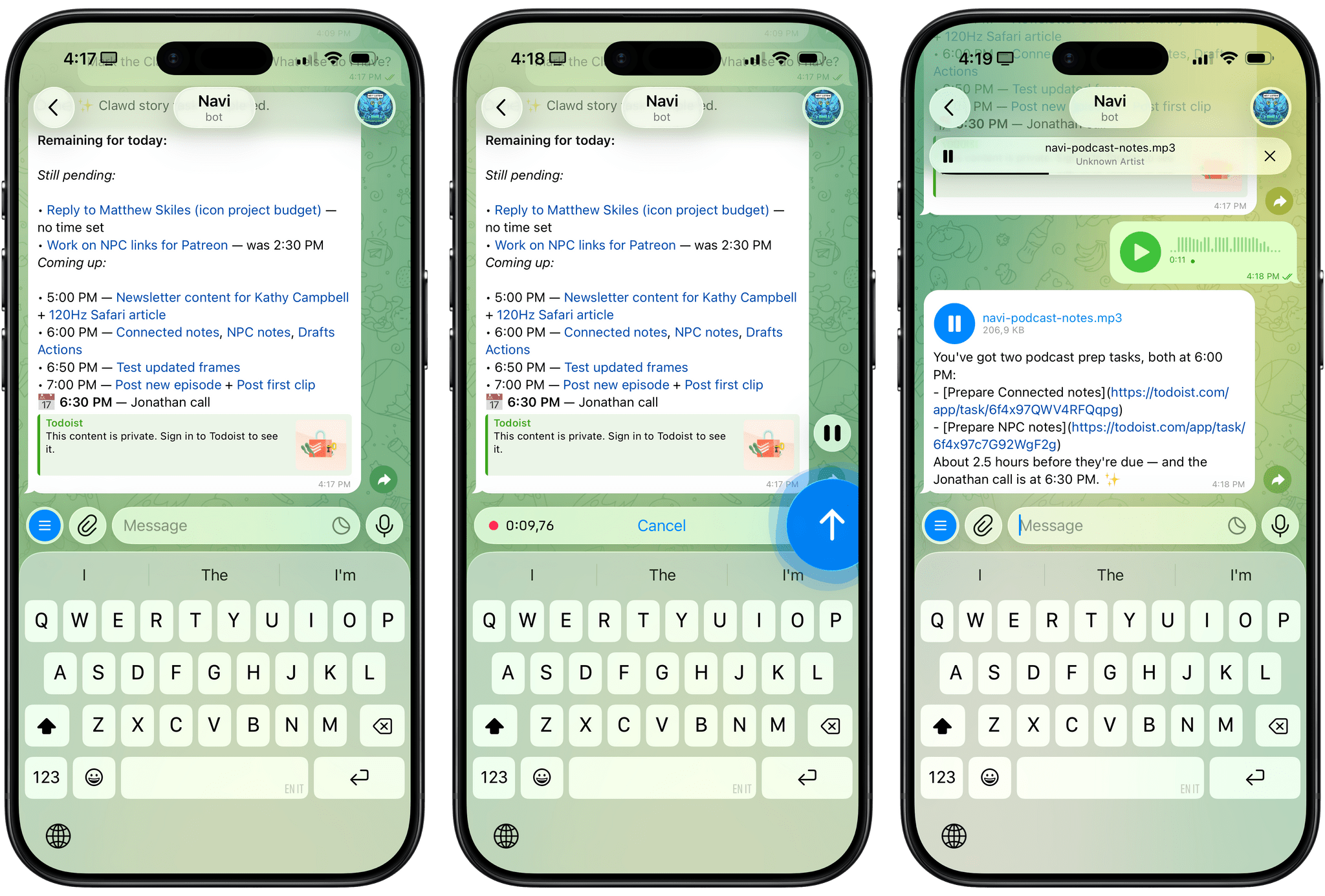
For the past week or so, I’ve been working with a digital assistant that knows my name, my preferences for my morning routine, how I like to use Notion and Todoist, but which also knows how to control Spotify and my Sonos speaker, my Philips Hue lights, as well as my Gmail. It runs on Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 model, but I chat with it using Telegram. I called the assistant Navi (inspired by the fairy companion of Ocarina of Time, not the besieged alien race in James Cameron’s sci-fi film saga), and Navi can even receive audio messages from me and respond with other audio messages generated with the latest ElevenLabs text-to-speech model. Oh, and did I mention that Navi can improve itself with new features and that it’s running on my own M4 Mac mini server?
If this intro just gave you whiplash, imagine my reaction when I first started playing around with OpenClaw, the incredible open-source project by Peter Steinberger (a name that should be familiar to longtime MacStories readers) that’s become very popular in certain AI communities over the past few weeks. I kept seeing OpenClaw being mentioned by people I follow; eventually, I gave in to peer pressure, followed the instructions provided by the funny crustacean mascot on the app’s website, installed OpenClaw on my new M4 Mac mini (which is not my main production machine), and connected it to Telegram.
To say that OpenClaw has fundamentally altered my perspective of what it means to have an intelligent, personal AI assistant in 2026 would be an understatement. I’ve been playing around with OpenClaw so much, I’ve burned through 180 million tokens on the Anthropic API (yikes), and I’ve had fewer and fewer conversations with the “regular” Claude and ChatGPT apps in the process. Don’t get me wrong: OpenClaw is a nerdy project, a tinkerer’s laboratory that is not poised to overtake the popularity of consumer LLMs any time soon. Still, OpenClaw points at a fascinating future for digital assistants, and it’s exactly the kind of bleeding-edge project that MacStories readers will appreciate.
Apple Confirms AI Partnership with Google
Apple has confirmed to CNBC that it has entered into a multi-year partnership with Google to use the search giant’s models and cloud technology for its own AI efforts. According to an unnamed Apple spokesperson:
After careful evaluation, we determined that Google’s technology provides the most capable foundation for Apple Foundation Models and we’re excited about the innovative new experiences it will unlock for our users.
The report still leaves many questions unanswered, including how Gemini fits in with Apple’s own Foundation Models and whether and to what extent Apple will rely on Google hardware. However, after months of speculation and reports from Mark Gurman at Bloomberg that Apple and Google were negotiating, it looks like we’re on the cusp of Apple’s AI strategy coming into better focus.
UPDATE:
Subsequent to the statement made by Apple to CNBC, Apple and Google released a slightly more detailed joint statement that Google published on X:
Apple and Google have entered into a multi-year collaboration under which the next generation of Apple Foundation Models will be based on Google’s Gemini models and cloud technology. These models will help power future Apple Intelligence features, including a more personalized Siri coming this year.
After careful evaluation, Apple determined that Google’s Al technology provides the most capable foundation for Apple Foundation Models and is excited about the innovative new experiences it will unlock for Apple users. Apple Intelligence will continue to run on Apple devices and Private Cloud Compute, while maintaining Apple’s industry-leading privacy standards.
So, while the Apple Foundation Models that power Apple Intelligence will be based on Gemini and unspecified cloud technology, Apple Intelligence features themselves, including more personalized Siri, will continue to run locally on Apple devices and on Apple’s Private Cloud Compute to maintain user privacy.
How I Revived My Decade-Old App with Claude Code
Every holiday season, Federico and I spend our downtime on nerd projects. This year, both of us spent a lot of that time building tools for ourselves with Claude Code in what developed into a bit of a competition as we each tried to one-up the other’s creations. We’ll have more on what we’ve been up to on AppStories, MacStories, and for Club members soon, but today, I wanted to share an experiment I ran last night that I think captures a very personal and potentially far-reaching slice of what tools like Claude Code can enable.
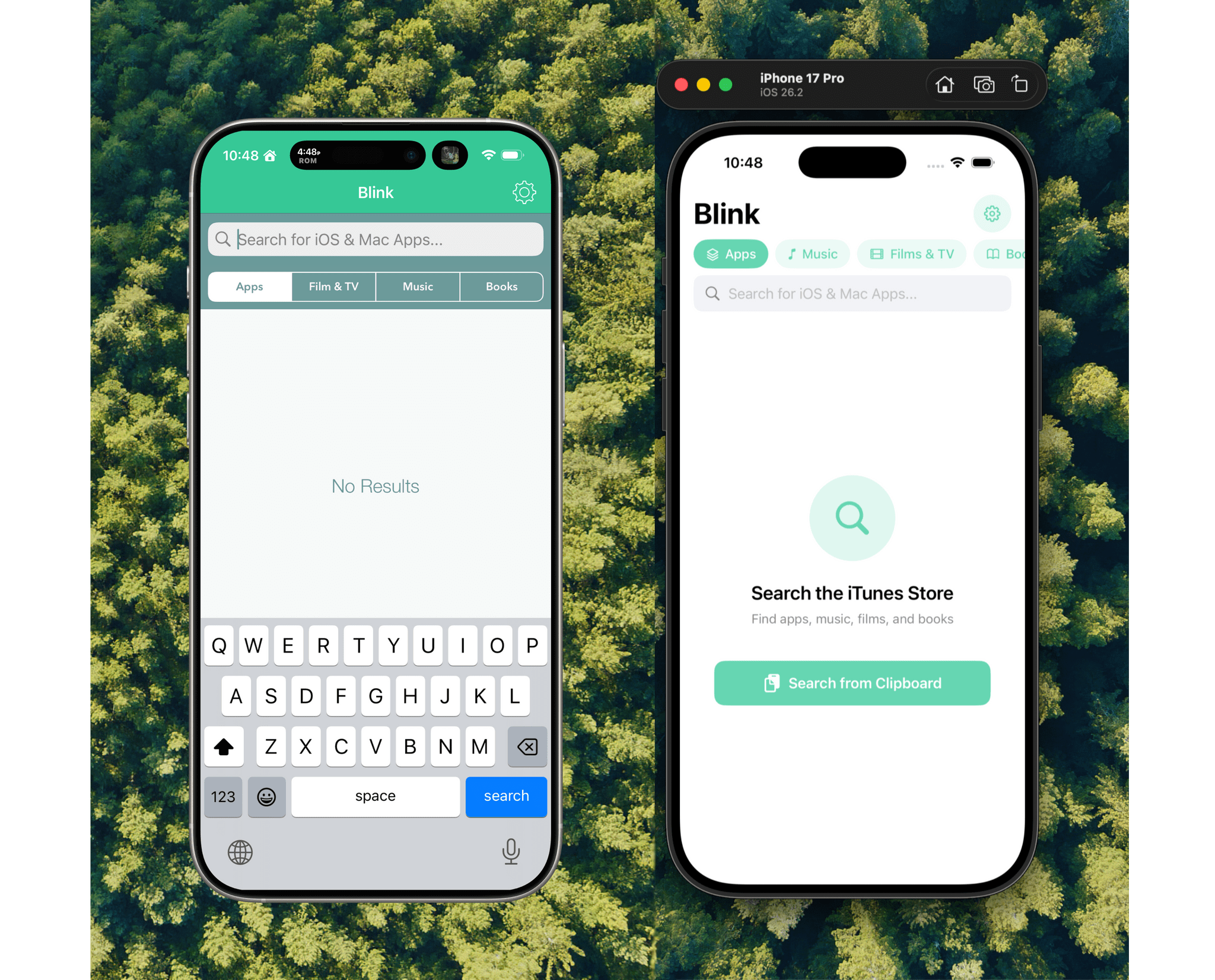
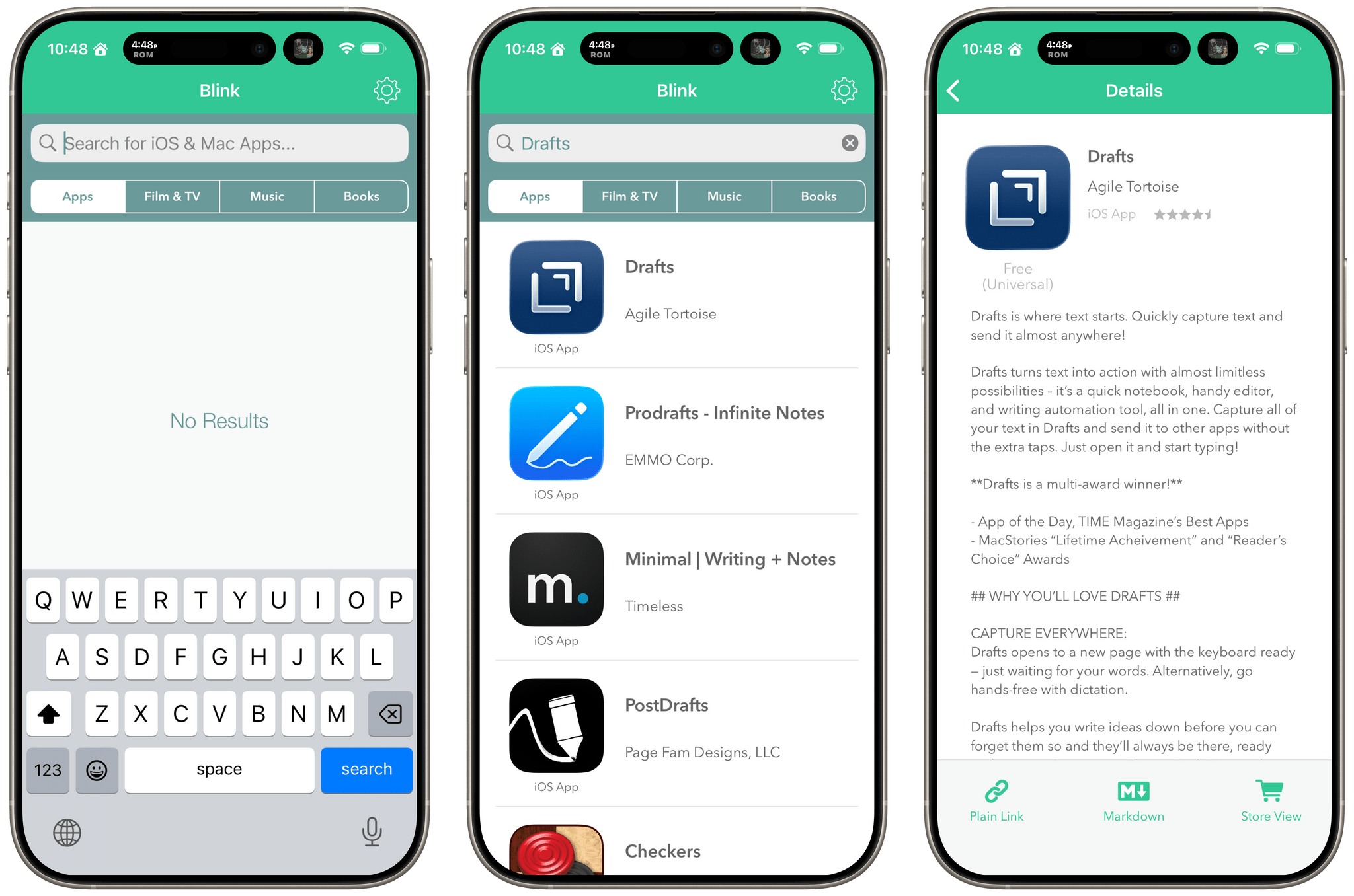
Before I wrote at MacStories, I made a few apps, including Blink, which generated affiliate links for Apple’s media services. The app had a good run from 2015-2017, but I pulled it from the App Store when Apple ended its affiliate program for apps because that was the part of the app that was used the most. Since then, the project has sat in a private GitHub repo untouched.
Last night, I was sitting on the couch working on a Safari web extension when I opened GitHub and saw that old Blink code, which sparked a thought. I wondered whether Claude Code could update Blink to use Swift and SwiftUI with minimal effort on my part. I don’t have any intention of re-releasing Blink, but I couldn’t shake the “what if” rattling in my head, so I cloned the repo and put Claude to work.
OpenAI Opens Up ChatGPT App Submissions to Developers
Announced earlier this year at OpenAI’s DevDay, developers may now submit ChatGPT apps for review and publication. OpenAI’s blog post explains that:
Apps extend ChatGPT conversations by bringing in new context and letting users take actions like order groceries, turn an outline into a slide deck, or search for an apartment.
Under the hood, OpenAI is using MCP, Model Context Protocol, which was pioneered by Anthropic late last year and donated to the Agentic AI Foundation last week.
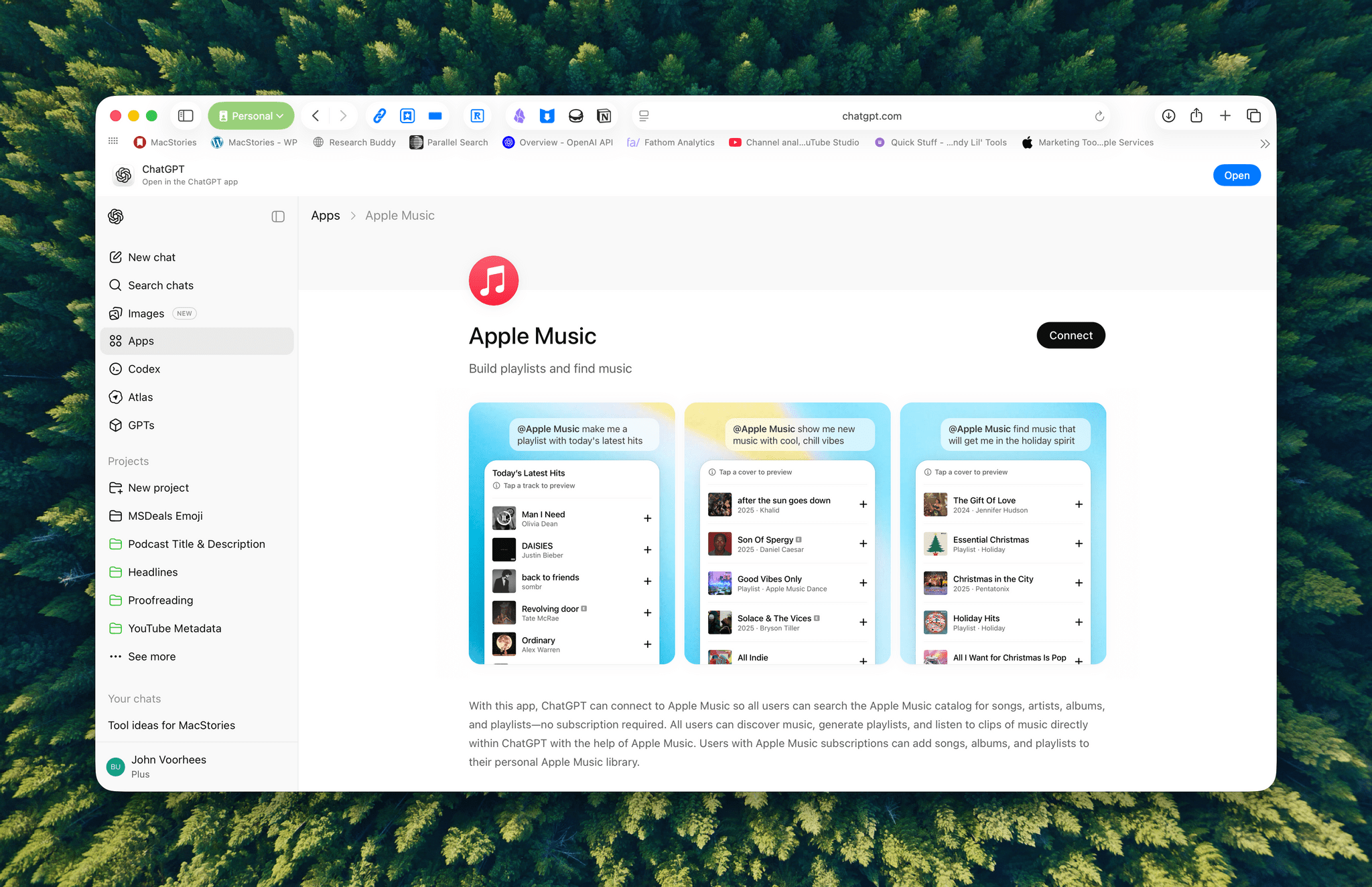
Apps are currently available in the web version of ChatGPT from the sidebar or tools menu and, once connected, can be accessed by @mentioning them. Early participants include Adobe, which preannounced its apps last week, Apple Music, Spotify, Zillow, OpenTable, Figma, Canva, Expedia, Target, AllTrails, Instacart, and others.
I was hoping the Apple Music app would allow me to query my music library directly, but that’s not possible. Instead, it allows ChatGPT to do things like search Apple Music’s full catalog and generate playlists, which is useful but limited.
Currently, there’s no way for developers to complete transactions inside ChatGPT. Instead, sales can be kicked to another app or the web, although OpenAI says it is exploring ways to offer transactions inside ChatGPT. Developers who want to submit an app must follow OpenAI’s app submission guidelines (sound familiar?) and can learn more from a variety of resources that OpenAI has made available.
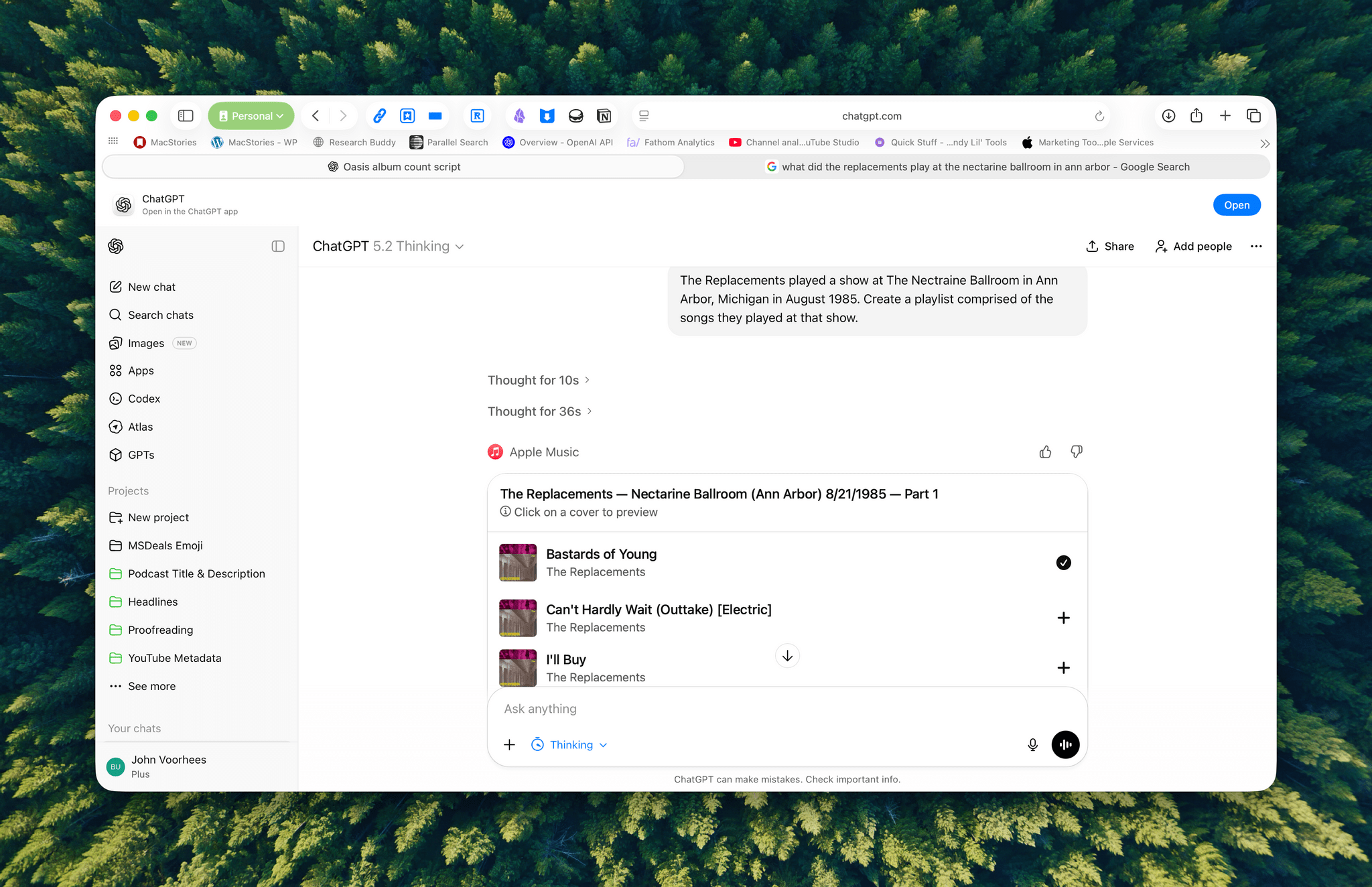
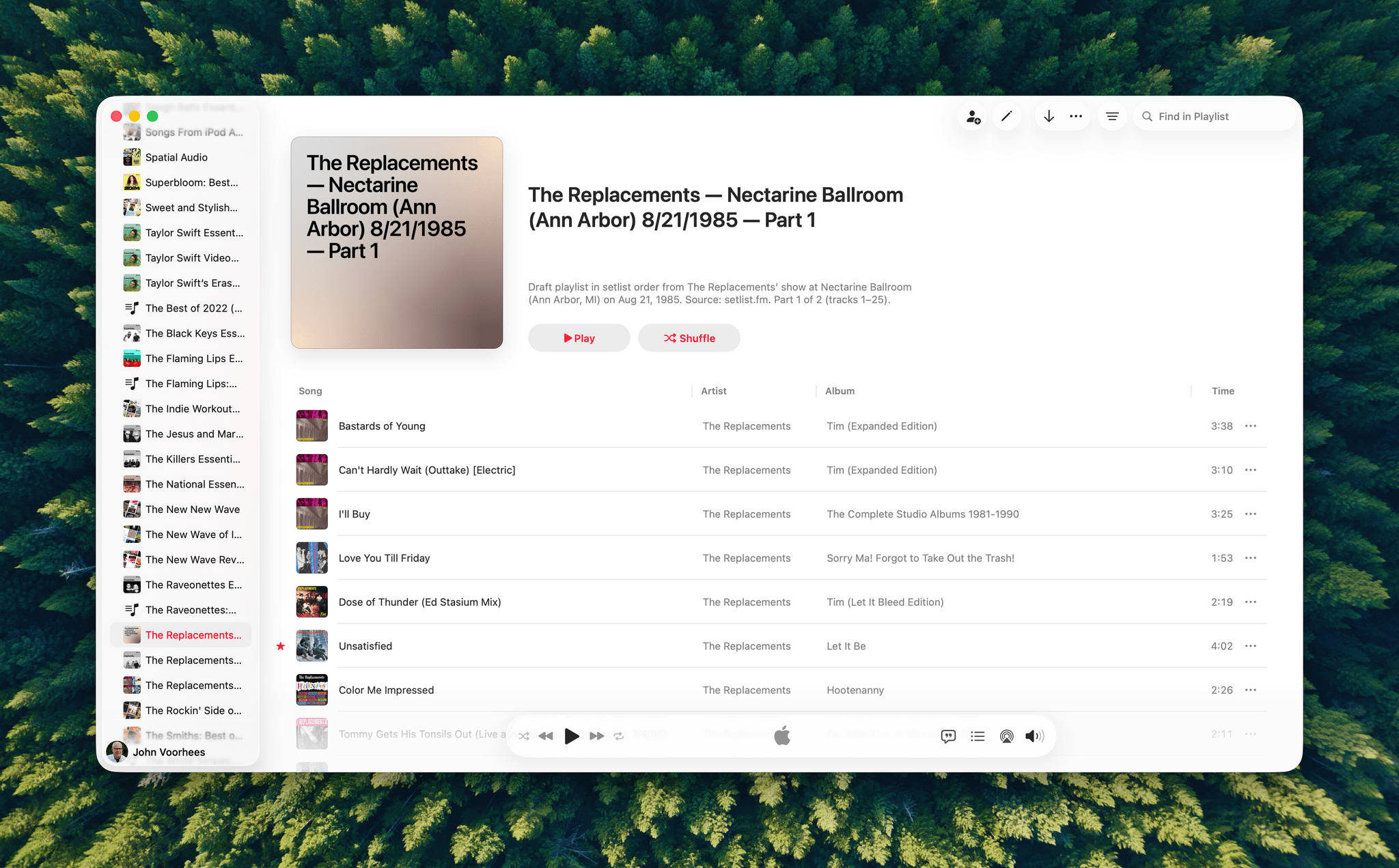
I haven’t spent a lot of time with the apps that are available, but despite the lack of access to your library, the Apple Music integration can be useful when combined with ChatGPT’s world knowledge. I asked it to create a playlist of the songs that The Replacements played at a show I saw in 1985, and while I don’t recall the exact setlist, ChatGPT matched what’s on Setlist.fm, a user-maintained wiki of live shows. I could have made this playlist myself, but it was convenient to have ChatGPT do it instead, even if the Apple Music integration is limited to 25-song playlists, which meant that The Replacements’ setlist was split into two playlists.
We’re still in the early days of MCP, and participation by companies will depend on whether they can make incremental sales to users via ChatGPT. Still, there’s clearly potential for apps embedded in chatbots to take off.
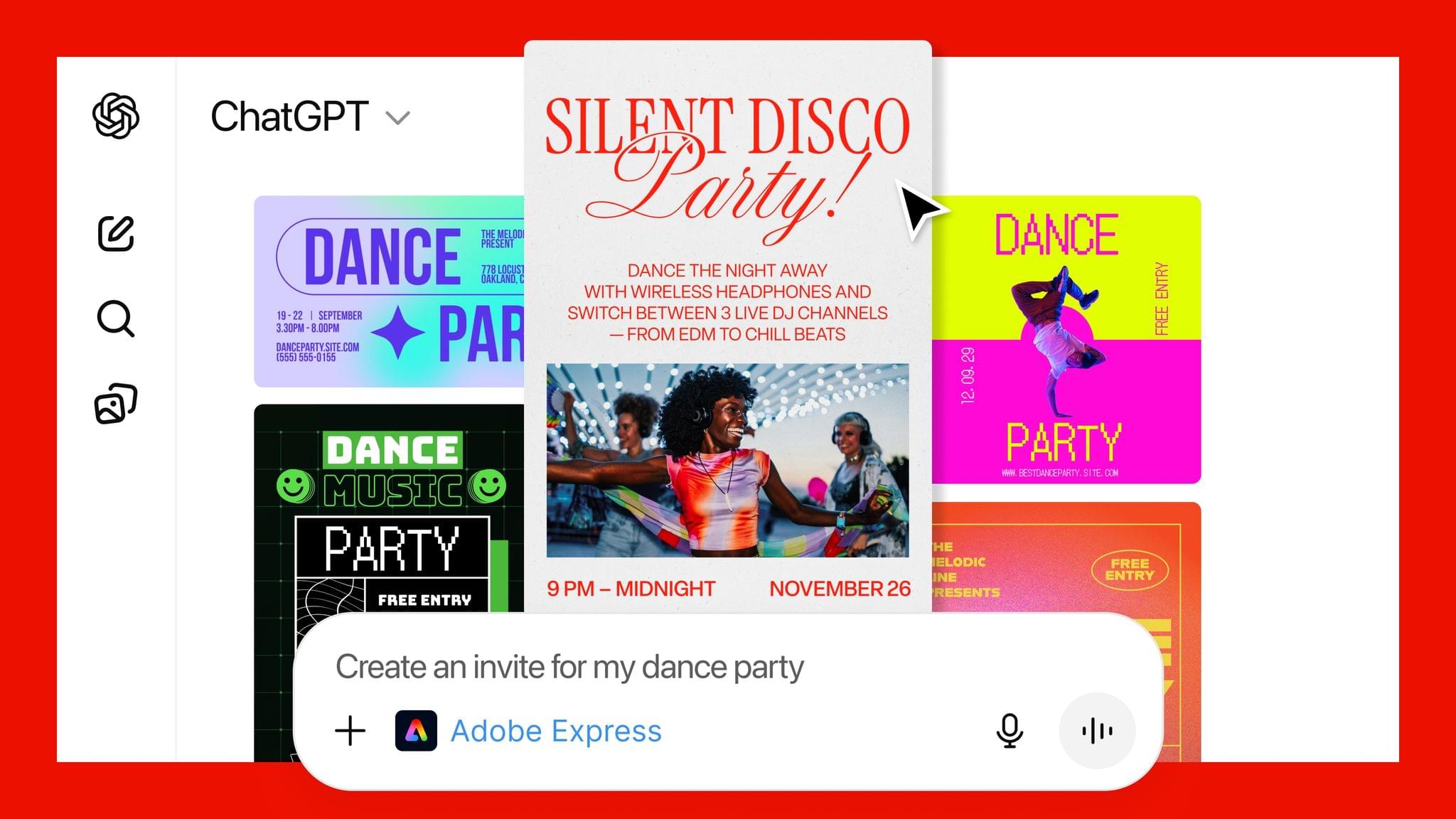
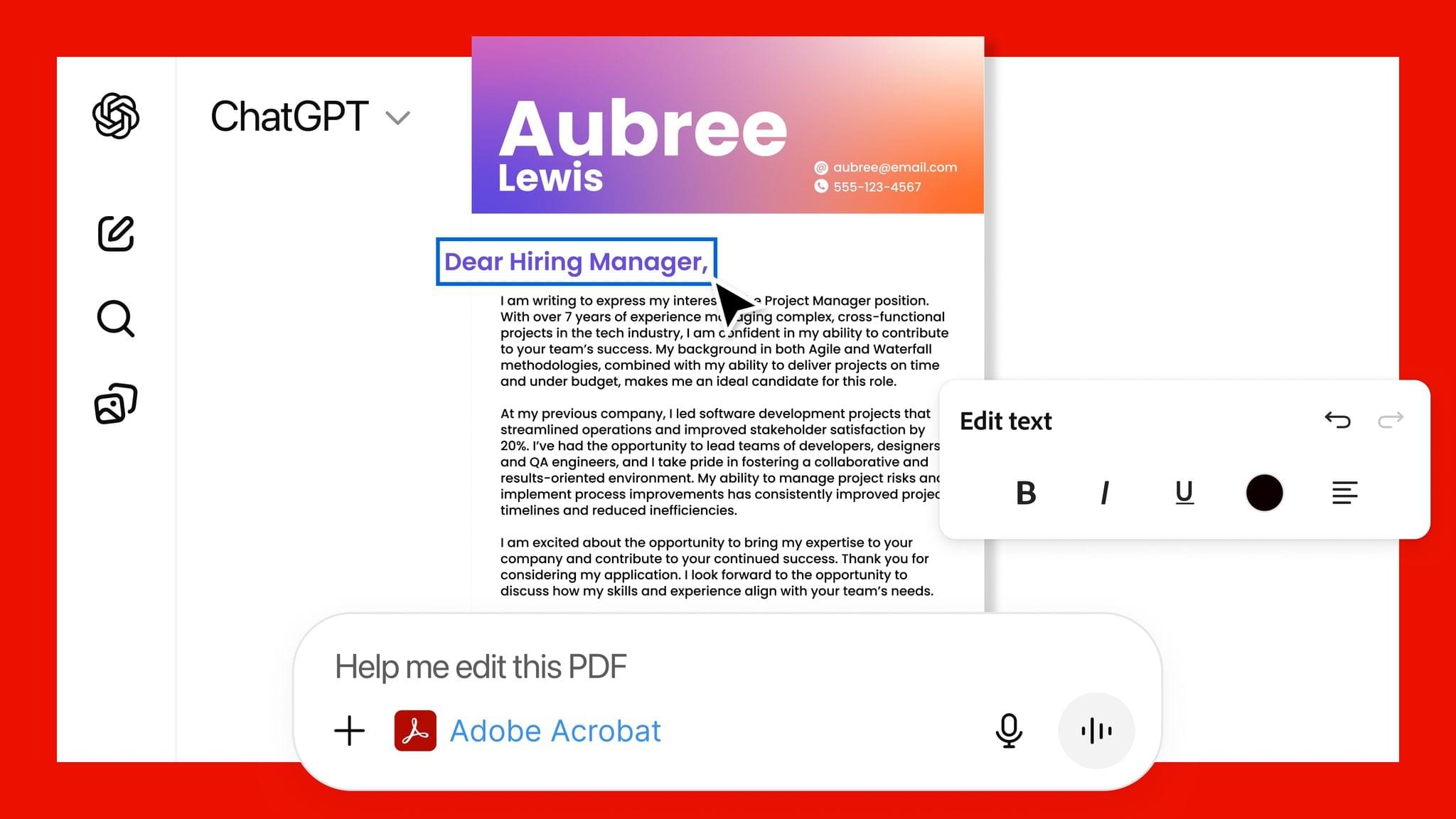
Adobe Announces Image and PDF Integration with ChatGPT
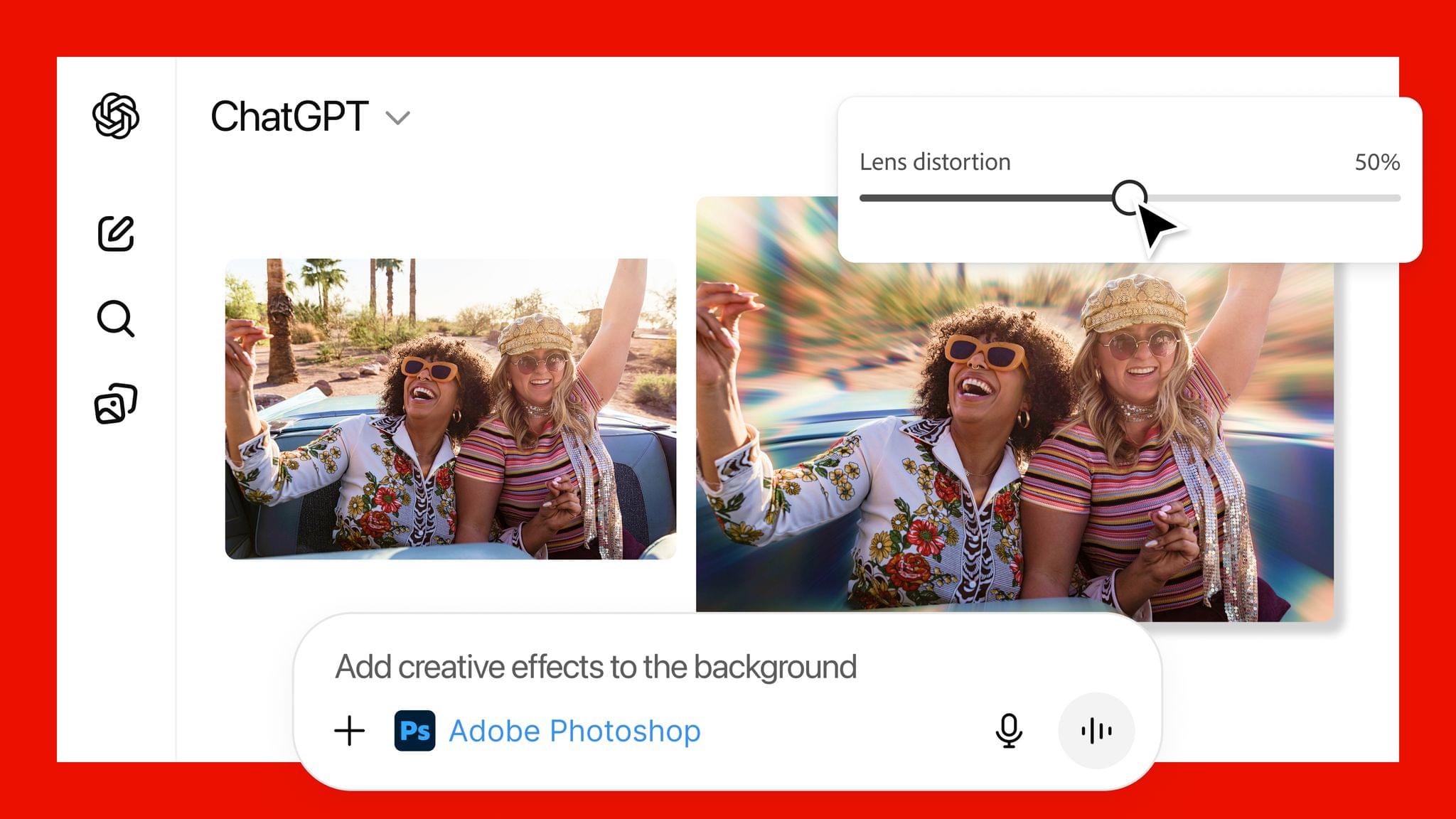
Adobe announced today that it has teamed up with OpenAI to give ChatGPT users access to Photoshop, Express, and Acrobat from inside the chatbot. The new integration is available starting today at no additional cost to ChatGPT users.
In a press release to Business Wire, Adobe explains that its three apps can be used by ChatGPT users to:
- Easily edit and uplevel images with Adobe Photoshop: Adjust a specific part of an image, fine tune image settings like brightness, contrast and exposure, and apply creative effects like Glitch and Glow – all while preserving the quality of the image.
- Create and personalize designs with Adobe Express: Browse Adobe Express’ extensive library of professional designs to find the best one for any moment, fill in the text, replace images, animate designs and iterate on edits – all directly inside the chat and without needing to switch to another app – to create standout content for any occasion.
- Transform and organize documents with Adobe Acrobat: Edit PDFs directly in the chat, extract text or tables, organize and merge multiple files, compress files and convert them to PDF while keeping formatting and quality intact. Acrobat for ChatGPT also enables people to easily redact sensitive details.
This strikes me as a savvy move by Adobe. Allowing users to request image and PDF edits and design documents with natural language prompts makes its tools more approachable. That could attract new users who later move to an Adobe subscription to get more control over their creations and Adobe’s other offerings.
From OpenAI’s standpoint, this is clearly a response to the consumer-facing Gemini features that Google has begun releasing, which include new image and video generation tools and reportedly caused Sam Altman to declare a “code red” inside the company. I understand the OpenAI freakout. Google has a huge user base and has been doing consumer products far longer than OpenAI, but I can’t say I’ve been very impressed with Gemini 3. Perhaps that’s simply because I don’t care for generative images and video, but these latest moves by Google and OpenAI make it clear that they see them as foundational to consumer-facing AI tools.
How Stu Maschwitz Vibe Coded His Way Into an App Rejection and What It Means for the Future of Apps→
This week on AppStories, Federico and I talked about the personal productivity tools we’ve built for ourselves using Claude. They’re hyper-specific scripts and plugins that aren’t likely to be useful to anyone but us, which is fine because that’s all they’re intended to be.
Stu Maschwitz took a different approach. He’s had a complex shortcut called Drinking Buddy for years that tracks alcohol consumption and calculates your Blood Alcohol Level using an established formula. But because he was butting up against the limits of what Shortcuts can do, he vibe coded an iOS version of Drinking Buddy.
Two things struck me about Maschwitz’s experience. First, the app he used to create Drinking Buddy for iOS was Bitrig, which Federico and I mentioned briefly on AppStories. His experience struck a chord with me:
It’s a bit like building an app by talking to a polite and well-meaning tech support agent on the phone — only their computer is down and they can’t test the app themselves.
But power through it, and you have an app.
That’s exactly how scripting with Claude feels. It compliments you on how smart you are, gets you 90% of the way to the finish line quickly, and then tortures you with the last 10%. That, in a nutshell, is coding with AI, at least for anyone with limited development skills, like myself.
But the second and more interesting lesson from Maschwitz’s post is what it portends for apps in general. App Review rejected Drinking Buddy’s Blood Alcohol Level calculation on the basis of Section 1.4, the Physical Harm rule.
Maschwitz appealed and was rejected, even though other Blood Alcohol Level apps are available on the App Store. However, instead of pushing the rejection with App Review further, Maschwitz turned to Lovable, another AI app creation tool, which generates web apps. With screenshots from his rejected iOS app and a detailed spec in hand, Maschwitz turned Drinking Buddy into a progressive web app.
Maschwitz’s experience is a great example of what we covered on AppStories. App creation tools, whether they generate native apps or web apps, are evolving rapidly. And, while they can be frustrating to use at times, are limited in what they can produce, and don’t solve a myriad of problems like customer support that we detail on AppStories, they’re getting better at code quickly. Whether you’re building for yourself, like we are at MacStories, or to share your ideas with others, like Stu Maschwitz, change is coming to apps. Some AI-generated apps will be offered in galleries inside the tools that created them, others will be designed for the web to avoid App Review, and some will likely live as perpetual TestFlight betas or scripts sitting on just one person’s computer, but regardless of the medium, bringing your ideas to life with code has never been more possible.
John Giannandrea’s Retirement From Apple Announced
Today Apple announced the retirement of John Giannandrea, the company’s senior vice president for Machine Learning and AI Strategy. Giannandrea will remain at Apple as an advisor until next spring.
News of Giannandrea’s retirement was paired with an announcement that Apple has hired Amar Subramanya as vice president of AI. Subramanya, who worked at Microsoft since this past summer, previously worked at Google for 16 years on projects including the company’s Gemini Assistant. Subramanya will take the lead on Apple Foundation Models, ML research, and AI Safety and Evaluation, while other areas of Giannandrea’s work will be inherited by Sabih Khan and Eddy Cue.
Apple CEO Tim Cook thanked Giannandrea for his tenure at the company:
We are thankful for the role John played in building and advancing our AI work, helping Apple continue to innovate and enrich the lives of our users. AI has long been central to Apple’s strategy, and we are pleased to welcome Amar to Craig’s leadership team and to bring his extraordinary AI expertise to Apple. In addition to growing his leadership team and AI responsibilities with Amar’s joining, Craig has been instrumental in driving our AI efforts, including overseeing our work to bring a more personalized Siri to users next year.
Given the troubled history of Apple’s AI efforts, the retirement of Giannandrea isn’t surprising. It will be interesting to see if Subramanya settles into his new role given the frequency with which top AI talent tends to turn over in the tech industry.
Why is ChatGPT for Mac So Good?→
Great post by Allen Pike on the importance of a great app experience for modern LLMs, which I recently wrote about. He opens with this line, which is a new axiom I’m going to reuse extensively:
A model is only as useful as its applications.
And on ChatGPT for Mac specifically:
The app does a good job of following the platform conventions on Mac. That means buttons, text fields, and menus behave as they do in other Mac apps. While ChatGPT is imperfect on both Mac and web, both platforms have the finish you would expect from a daily-use tool.
[…]
It’s easier to get a polished app with native APIs, but at a certain scale separate apps make it hard to rapidly iterate a complex enterprise product while keeping it in sync on each platform, while also meeting your service and customer obligations. So for a consumer-facing app like ChatGPT or the no-modifier Copilot, it’s easier to go native. For companies that are, at their core, selling to enterprises, you get Electron apps.
I don’t hate Electron as much as others in our community, but I can’t deny that ChatGPT is one of the nicest AI apps for Mac I’ve used. The other is the recently updated BoltAI. And they’re both native Mac apps.