In addition to Kimi K2 (which I recently wrote about here) and GLM-4.6 (which will become an option on Cerebras in a few days, when I’ll play around with it), one of the more interesting open-source LLM releases out of China lately is MiniMax M2. This MoE model (230B parameters, 10B activated at any given time) claims to reach 90% of the performance of Sonnet 4.5…at 8% the cost. You can read more about the model here; Simon Willison blogged about it here; you can also test it with MLX on an Apple silicon Mac.
What I find especially interesting about M2 is that it’s the first model to support interleaved thinking steps in between responses and tool calls, which is something that Anthropic pioneered with Claude Sonnet 4 back in May. Here’s Skyler Miao, head of engineering at MiniMax, in a post on X (unfortunately, most of the open-source AI community is only active there):
As we work more closely with partners, we’ve been surprised how poorly community support interleaved thinking, which is crucial for long, complex agentic tasks. Sonnet 4 introduced it 5 months ago, but adoption is still limited.
We think it’s one of the most important features for agentic models: it makes great use of test-time compute.
The model can reason after each tool call, especially when tool outputs are unexpected. That’s often the hardest part of agentic jobs: you can’t predict what the env returns. With interleaved thinking, the model could reason after get tool outputs, and try to find out a better solution.
We’re now working with partners to enable interleaved thinking in M2 — and hopefully across all capable models.
I’ve been using Claude as my main “production” LLM for the past few months and, as I’ve shared before, I consider the fact that both Sonnet and Haiku think between steps an essential aspect of their agentic nature and integration with third-party apps.
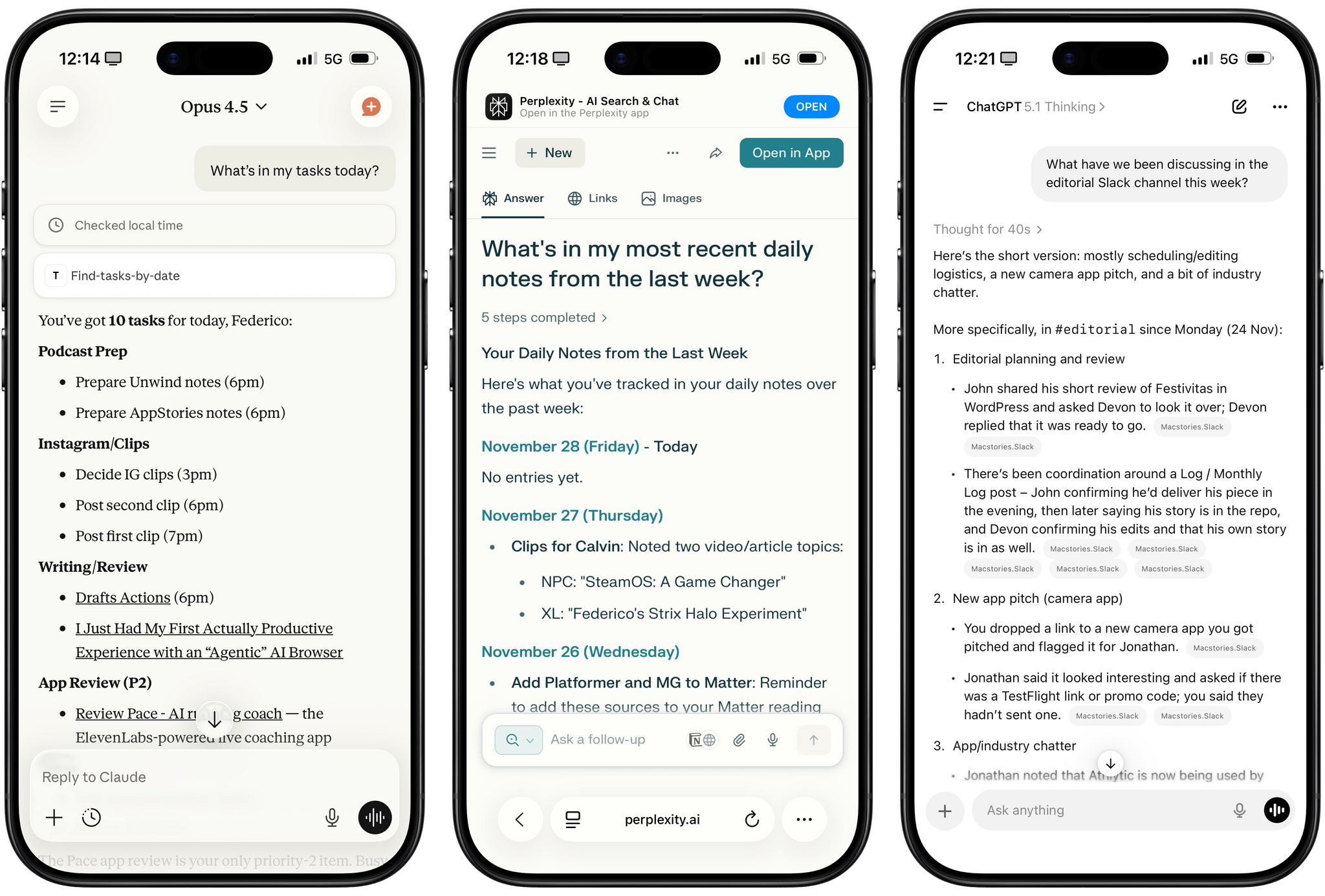
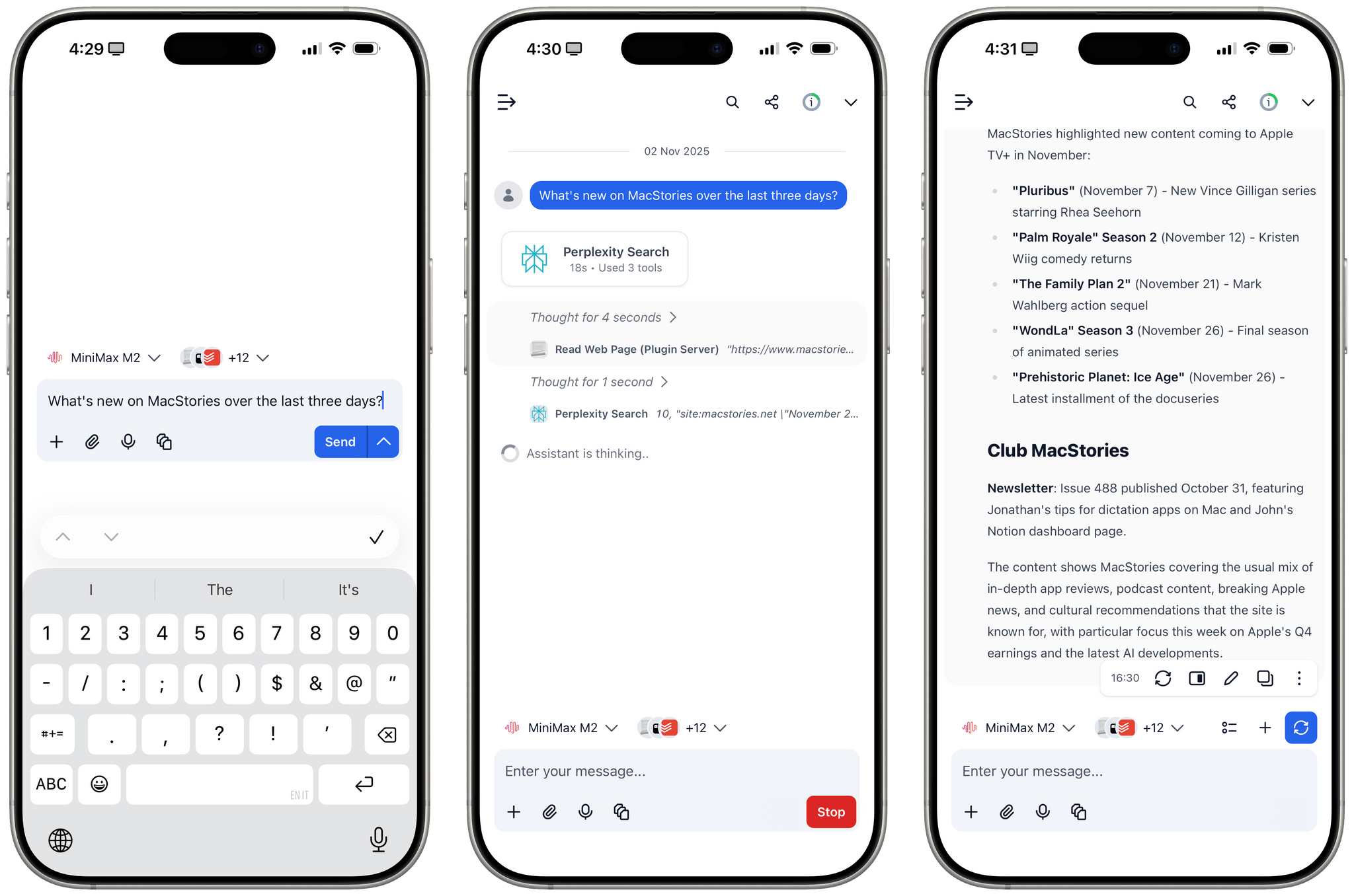
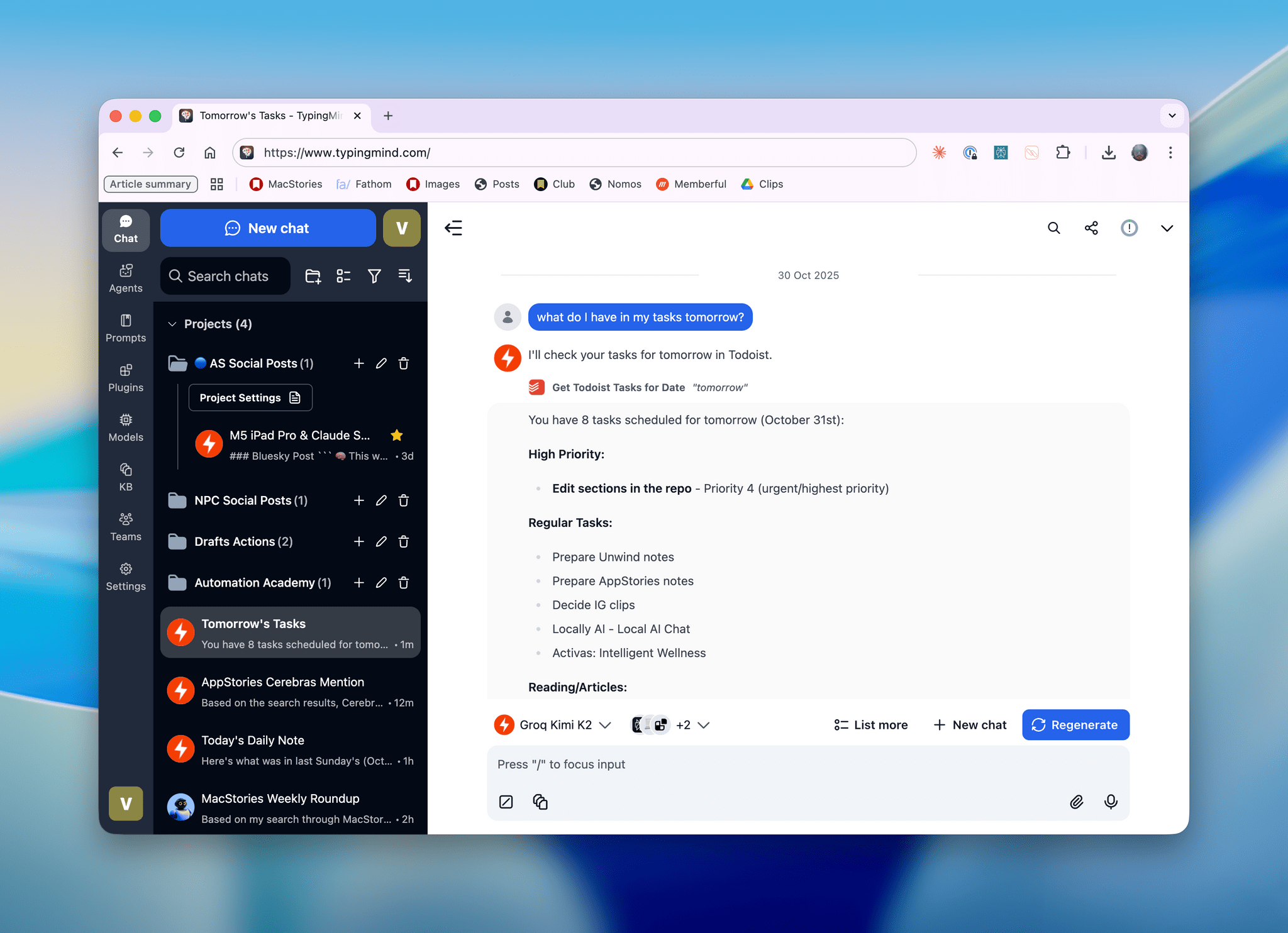
That being said, I have been testing MiniMax M2 on TypingMind in addition to Kimi K2 for the past week and it is, indeed, impressive. I plugged MiniMax M2 into TypingMind using their Anthropic-compatible endpoint; out of the box, the model worked with interleaved thinking and the several plugins I’ve built for myself in TypingMind using Claude. I haven’t used M2 for any vibe-coding tasks yet, but for other research or tool-based queries (like adding notes to Notion and tasks to Todoist), M2 effectively felt like a version of Sonnet not made by Anthropic.
Right now, MiniMax M2 isn’t hosted on any of the fast inference providers; I’ve accessed it via the official MiniMax API endpoint, whose inference speed isn’t that different from Anthropic’s cloud. The possibility of MiniMax M2 on Cerebras or Groq is extremely fascinating, and I hope it’s in the cards for the near future.