Today, the European Commission informed Apple that based on its preliminary investigation it has determined that the company is in violation of the Digital Markets Act. The EC has also opened a separate non-compliance procedure against Apple over the Core Technology Fee and other changes instituted earlier this year as part of its response to the DMA.
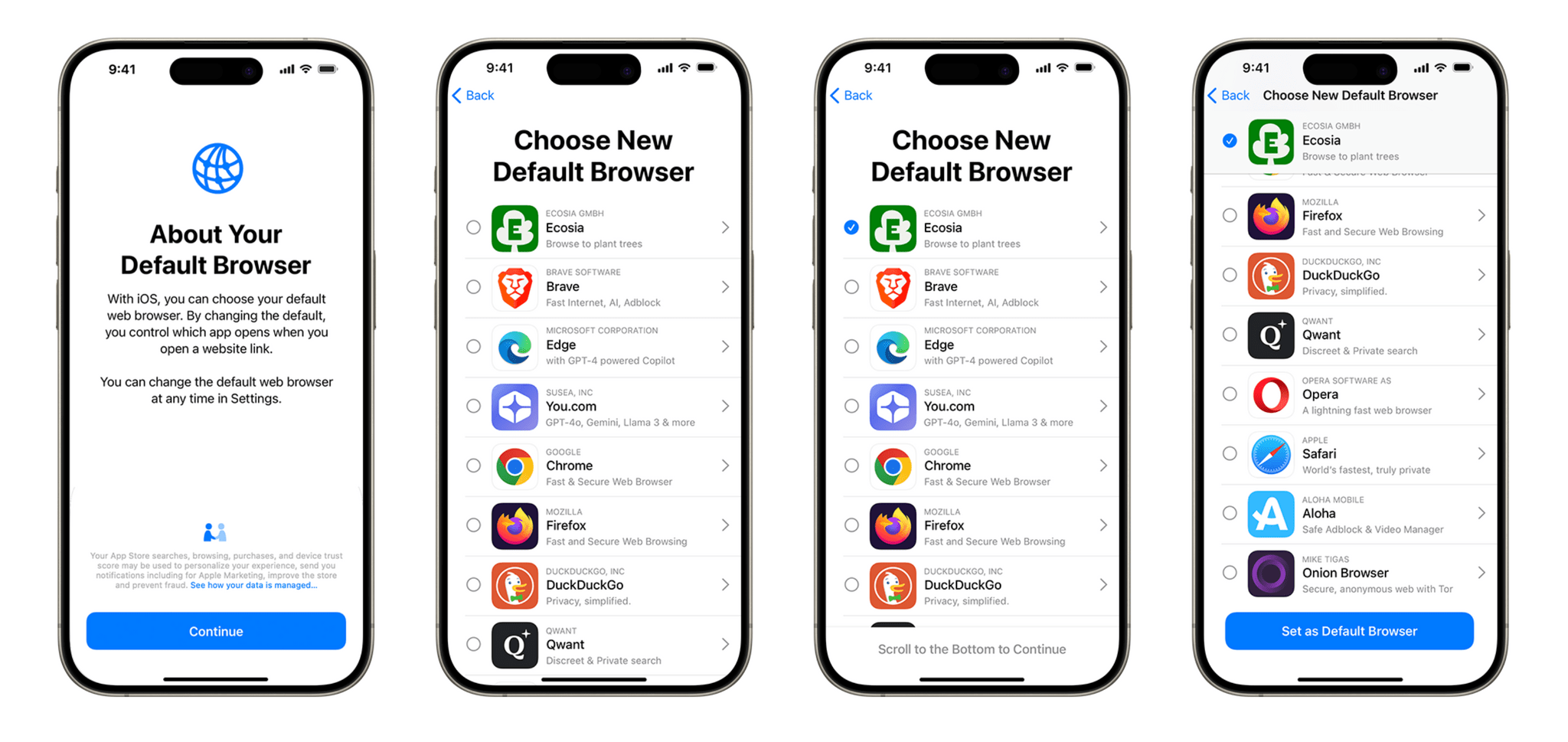
In particular, the EC’s preliminary findings take issue with Apple’s response to the DMA’s anti-steering provisions:
Apple currently has three sets of business terms governing its relationship with app developers, including the App Store’s steering rules. The Commission preliminarily finds that:
- None of these business terms allow developers to freely steer their customers. For example, developers cannot provide pricing information within the app or communicate in any other way with their customers to promote offers available on alternative distribution channels.
- Under most of the business terms available to app developers, Apple allows steering only through “link-outs”, i.e., app developers can include a link in their app that redirects the customer to a web page where the customer can conclude a contract. The link-out process is subject to several restrictions imposed by Apple that prevent app developers from communicating, promoting offers and concluding contracts through the distribution channel of their choice.
- Whilst Apple can receive a fee for facilitating via the AppStore the initial acquisition of a new customer by developers, the fees charged by Apple go beyond what is strictly necessary for such remuneration. For example, Apple charges developers a fee for every purchase of digital goods or services a user makes within seven days after a link-out from the app.
Apple may respond to the EC’s preliminary findings in writing. A final decision regarding compliance with the law is due by March 25, 2025, the one year anniversary of the beginning of DMA proceedings against Apple.
The EC has also opened a separate investigation regarding Apple’s compliance with Section 6(4) of the DMA, which provides that:
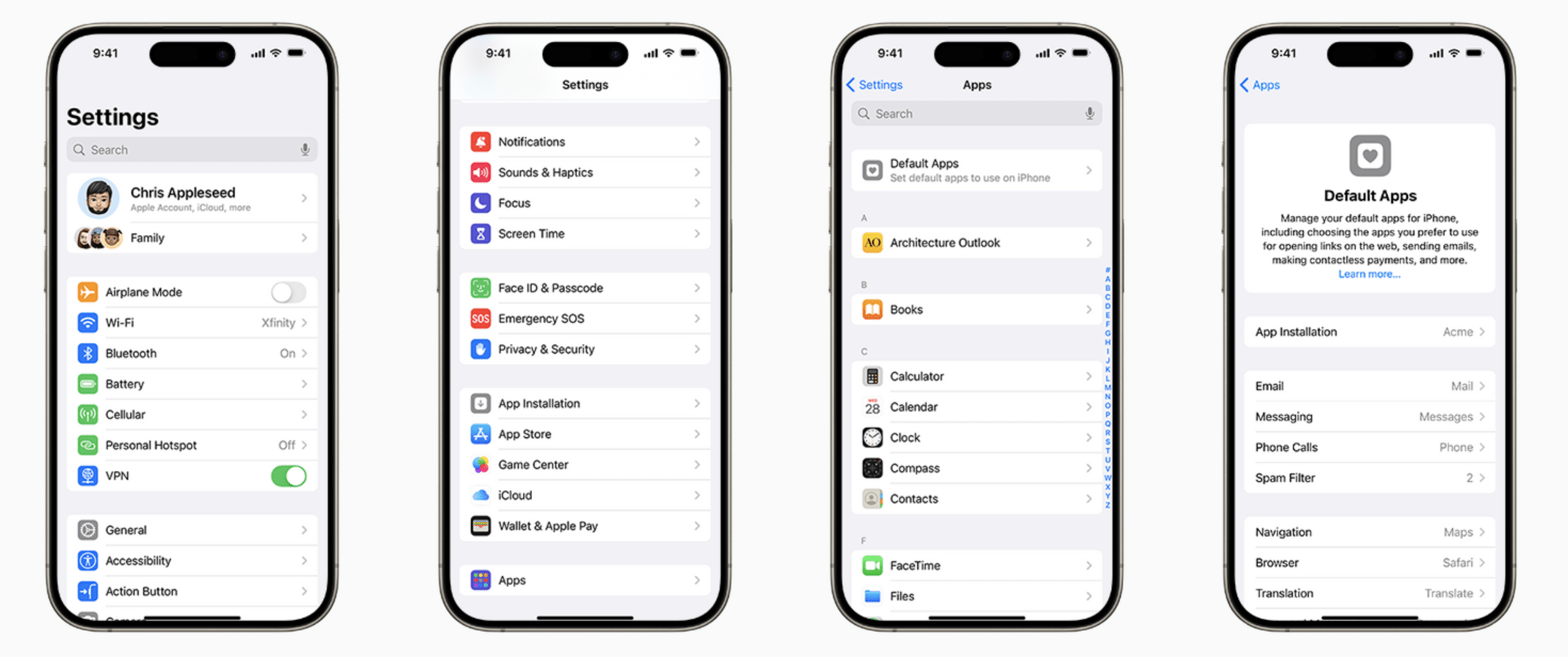
The gatekeeper shall allow and technically enable the installation and effective use of third-party software applications or software application stores using, or interoperating with, its operating system and allow those software applications or software application stores to be accessed by means other than the relevant core platform services of that gatekeeper. The gatekeeper shall, where applicable, not prevent the downloaded third-party software applications or software application stores from prompting end users to decide whether they want to set that downloaded software application or software application store as their default. The gatekeeper shall technically enable end users who decide to set that downloaded software application or software application store as their default to carry out that change easily.
The gatekeeper shall not be prevented from taking, to the extent that they are strictly necessary and proportionate, measures to ensure that third-party software applications or software application stores do not endanger the integrity of the hardware or operating system provided by the gatekeeper, provided that such measures are duly justified by the gatekeeper.
Furthermore, the gatekeeper shall not be prevented from applying, to the extent that they are strictly necessary and proportionate, measures and settings other than default settings, enabling end users to effectively protect security in relation to third-party software applications or software application stores, provided that such measures and settings other than default settings are duly justified by the gatekeeper.
Specifically, the EC says it will investigate whether the Core Technology Fee, the multi-step process for downloading apps from alternative app marketplaces, and the eligibility requirements for running an alternative app marketplace are ‘necessary and proportionate’ under the DMA. The EC also notes that it is continuing to investigate Apple’s process for validating apps and alternative app marketplaces.
None of this is particularly surprising, given the complexities of the provisions Apple put into place in the wake of the DMA. The ‘necessity and proportionality’ of Apple’s changes are, by their nature, subjective determinations. That makes the DMA hard to comply with, but it also leaves ample room for the EC and Apple to negotiate a resolution of their dispute over the DMA. It’s time for the parties to put this dispute to rest.








](https://cdn.macstories.net/banneras-1629219199428.png)