Update, January 30, 2026: The project has now been rebranded as OpenClaw (frankly, a much better name). The official website is openclaw.ai. Everything from this article still applies.
Update, January 27, 2026: Clawdbot has been renamed to Moltbot following a trademark-related request by Anthropic.
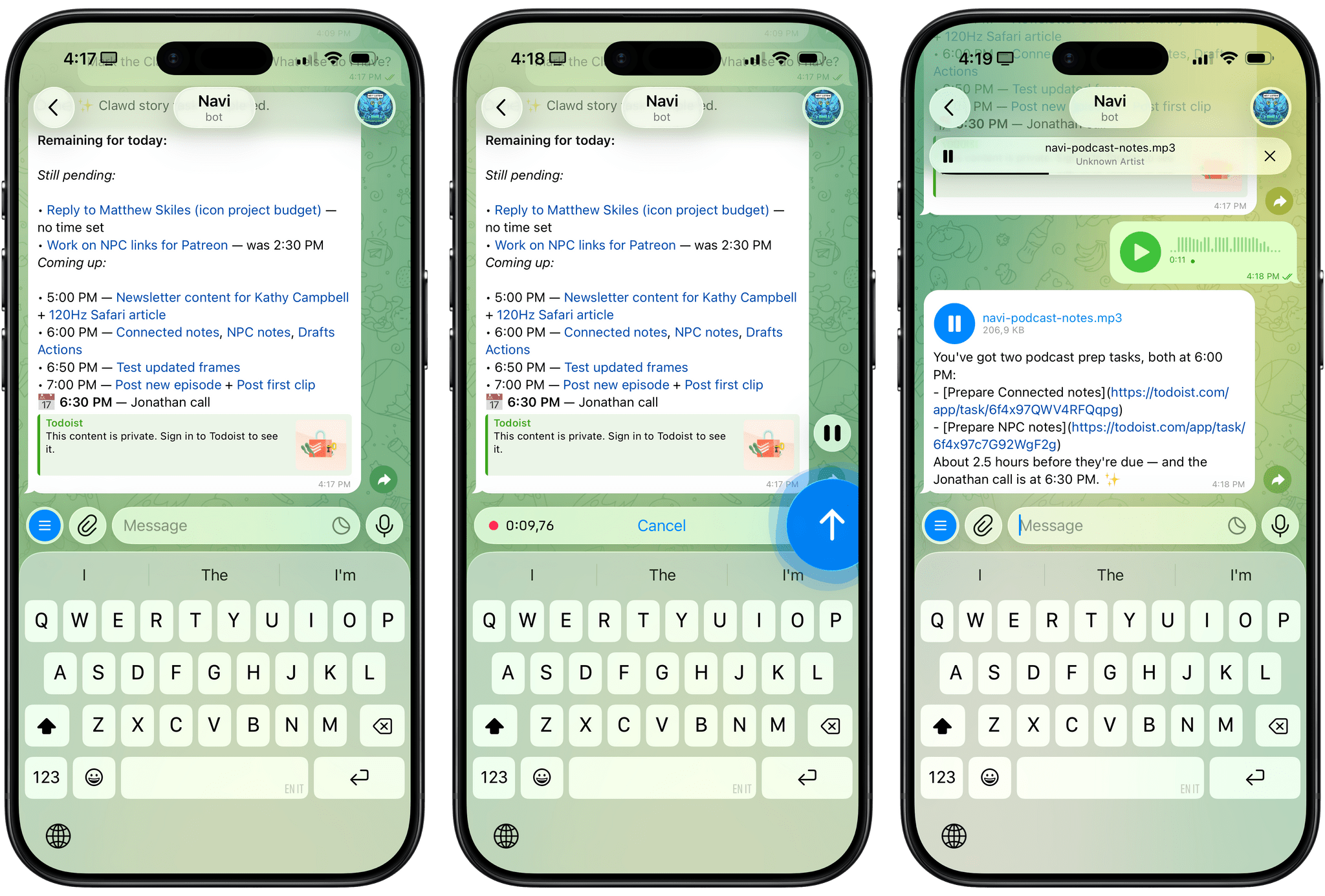
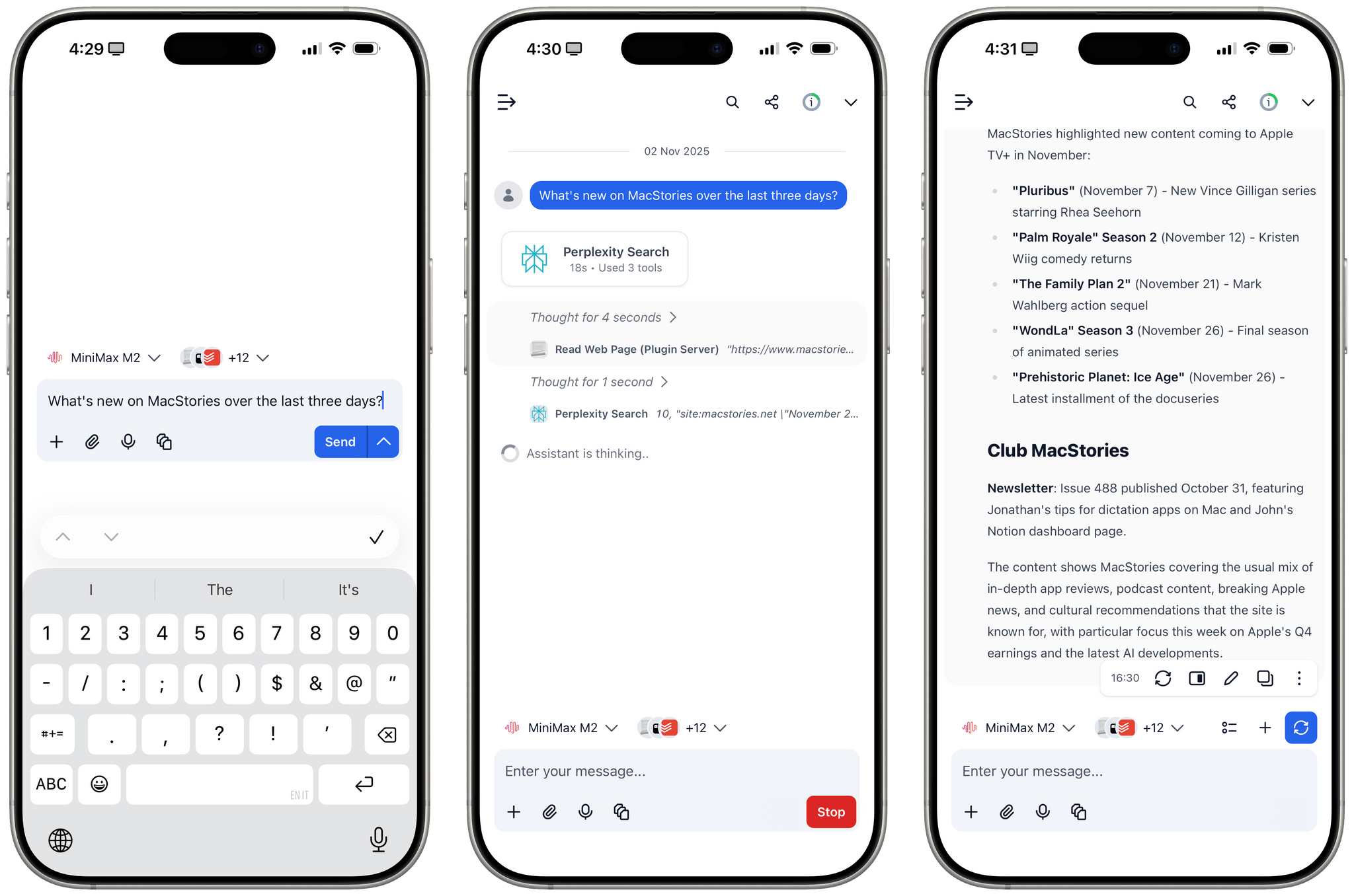
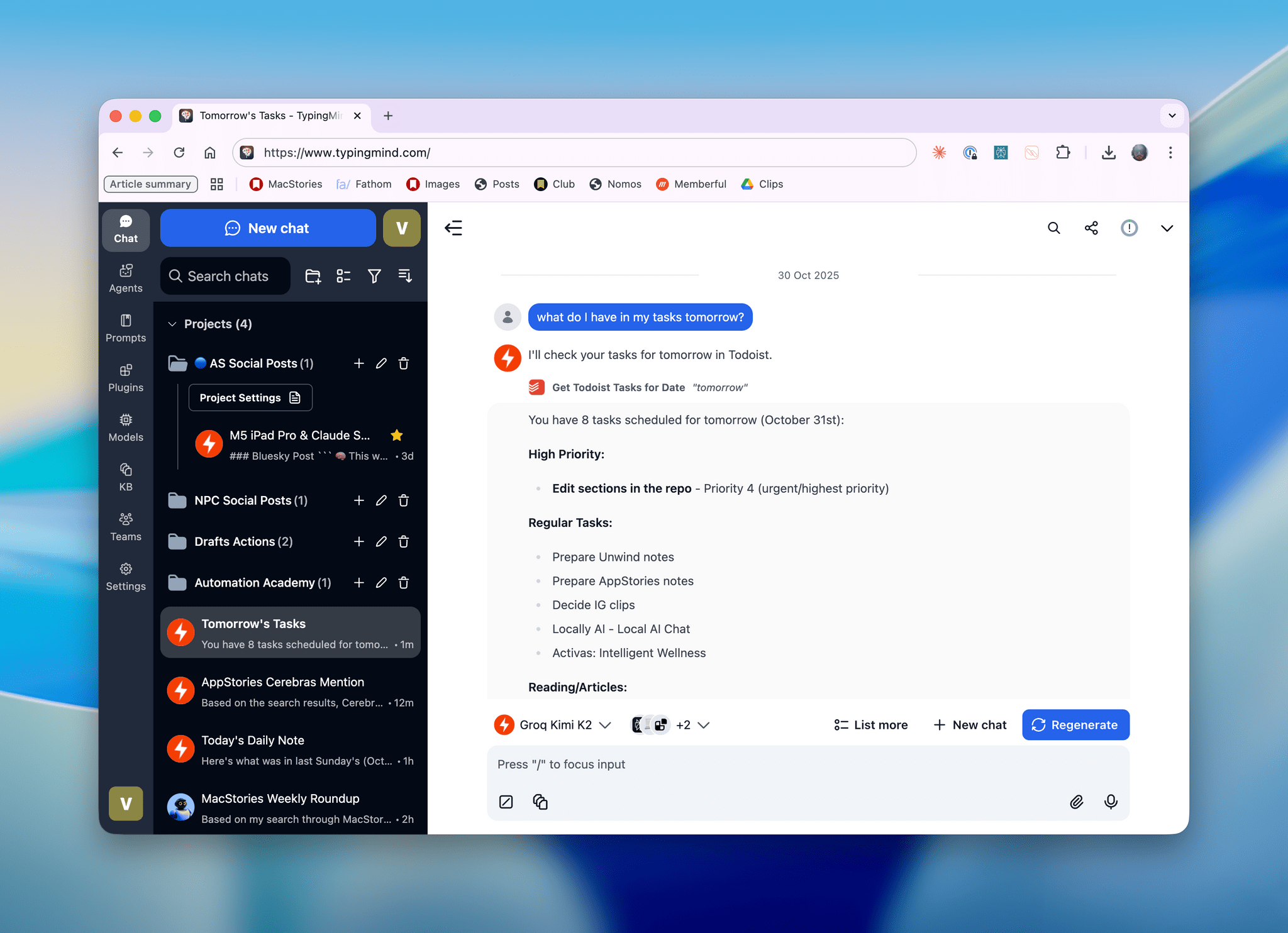
For the past week or so, I’ve been working with a digital assistant that knows my name, my preferences for my morning routine, how I like to use Notion and Todoist, but which also knows how to control Spotify and my Sonos speaker, my Philips Hue lights, as well as my Gmail. It runs on Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 model, but I chat with it using Telegram. I called the assistant Navi (inspired by the fairy companion of Ocarina of Time, not the besieged alien race in James Cameron’s sci-fi film saga), and Navi can even receive audio messages from me and respond with other audio messages generated with the latest ElevenLabs text-to-speech model. Oh, and did I mention that Navi can improve itself with new features and that it’s running on my own M4 Mac mini server?
If this intro just gave you whiplash, imagine my reaction when I first started playing around with Clawdbot, the incredible open-source project by Peter Steinberger (a name that should be familiar to longtime MacStories readers) that’s become very popular in certain AI communities over the past few weeks. I kept seeing Clawdbot being mentioned by people I follow; eventually, I gave in to peer pressure, followed the instructions provided by the funny crustacean mascot on the app’s website, installed Clawdbot on my new M4 Mac mini (which is not my main production machine), and connected it to Telegram.
To say that Clawdbot has fundamentally altered my perspective of what it means to have an intelligent, personal AI assistant in 2026 would be an understatement. I’ve been playing around with Clawdbot so much, I’ve burned through 180 million tokens on the Anthropic API (yikes), and I’ve had fewer and fewer conversations with the “regular” Claude and ChatGPT apps in the process. Don’t get me wrong: Clawdbot is a nerdy project, a tinkerer’s laboratory that is not poised to overtake the popularity of consumer LLMs any time soon. Still, Clawdbot points at a fascinating future for digital assistants, and it’s exactly the kind of bleeding-edge project that MacStories readers will appreciate.